Human Eye and Colourful World Class 10 Notes

Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World
Vidyakul's top academics have prepared a detailed, step-by-step CBSE NCERT notes for Class 10 scientific research. These notes provides students with explanations and tips for solving practice problems. Students can use NCERT notes to increase their confidence and achieve maximum test scores.
Class 10 Science Chapter 11 - Provided CBSE NCERT notes for the human eye and a colorful world. Students can refer to these notes to practice NCERT questions during preparation. Step-by-step notes are designed to increase conceptual clarity. Students will also understand the correct approach to problem solving. So read NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 11 notes to the Human Eye and the Colorful World.
CBSE CLASS 10th SCIENCE CH-11
Points to Remember
We have provided some of the crucial points related to Class 10 Science Chapter 11 as mentioned below:
Of all the sense organs, the human eye is the most significant one as it enables us to see the beautiful, colourful world around us. The eye is spherical in shape and has a diameter of 2.3 cm on average. The internal structure of the eye includes- the cornea, iris, pupil, lens, ciliary muscles, retina, nerve cells, optic nerve, yellow spot, aqueous and vitreous humor, and suspensory ligament.
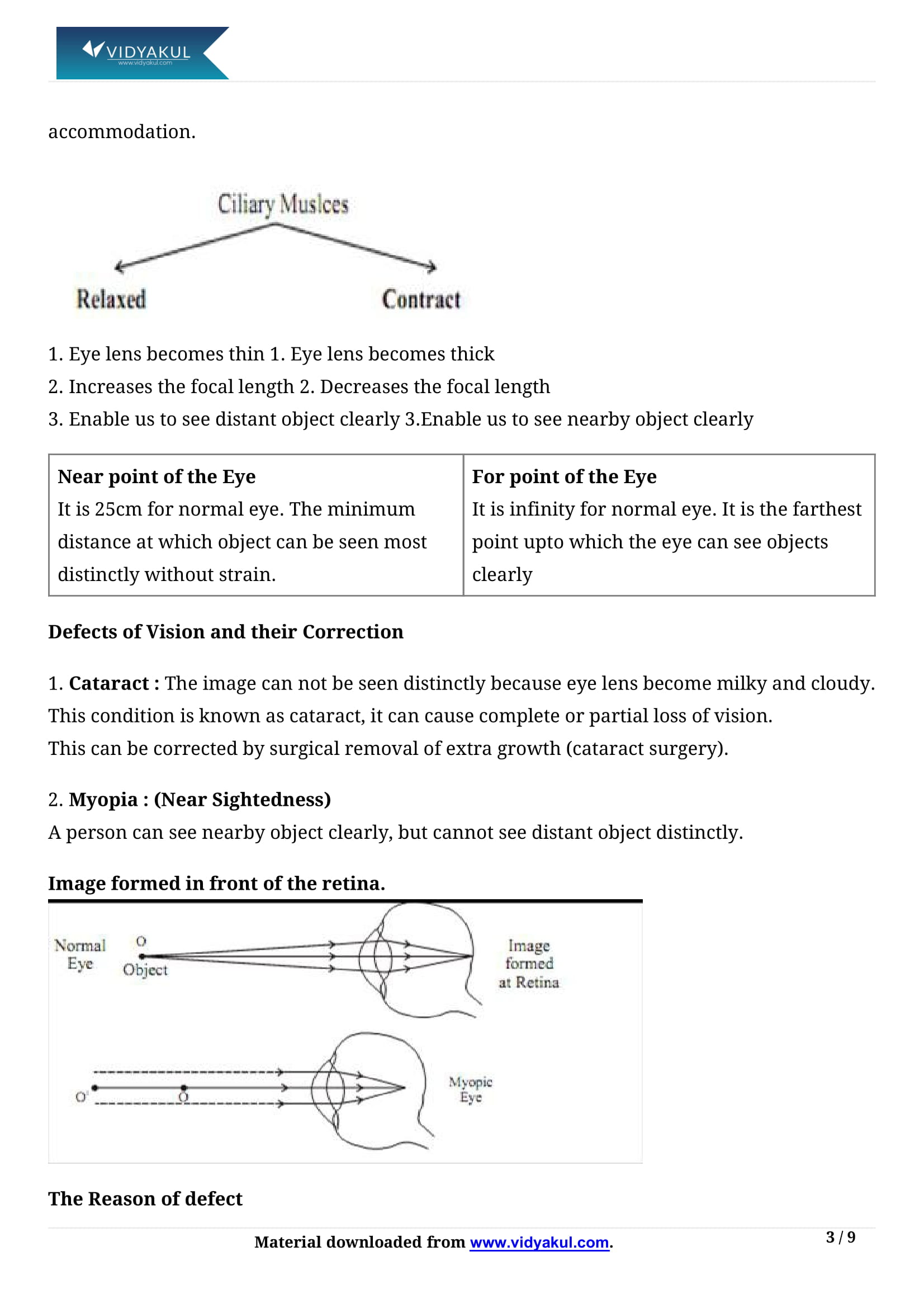
Myopia – This is also called as the short-sightedness. A person with this eye defect can only see the nearby objects clearly compared to distant objects. This condition can be corrected using a concave lens.
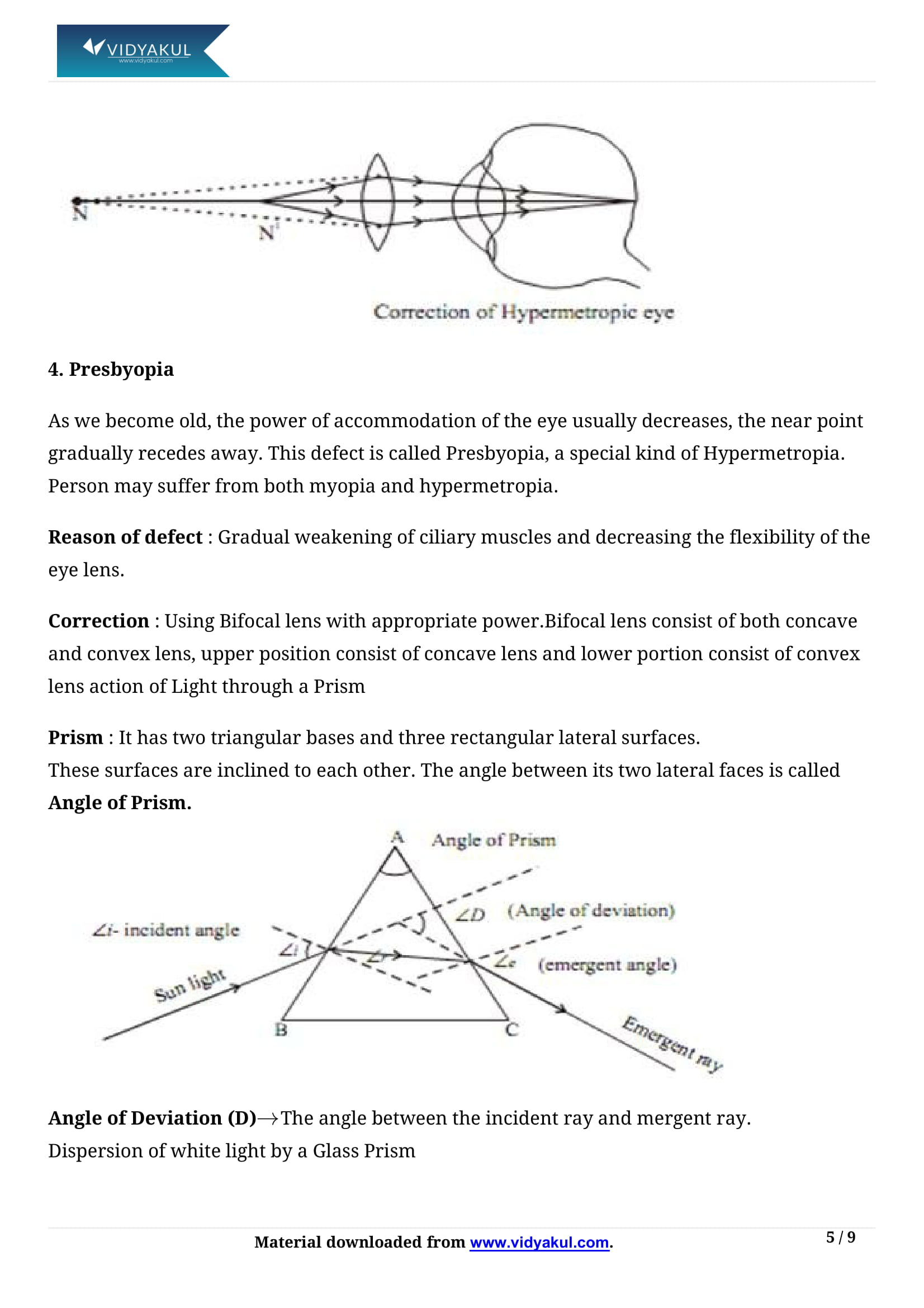
Hypermetropia – This is also called as the farsightedness. A person with this eye defect can only see the distant objects clearly compared to near objects. This condition can be corrected using a convex lens.
Presbyopia – This is an age-related condition caused due to the weakening of ciliary muscles, hardening of the lens, and reduced lens flexibility. A person with this defect usually finds difficulties to focus on nearby objects unable to read or write.
Cataract – This is an age-related condition caused due to the loss of transparency of the lens by erosion of lens proteins. It usually results in blurry vision, cloudy lenses and can be corrected by replacing the old lens with an artificial lens.
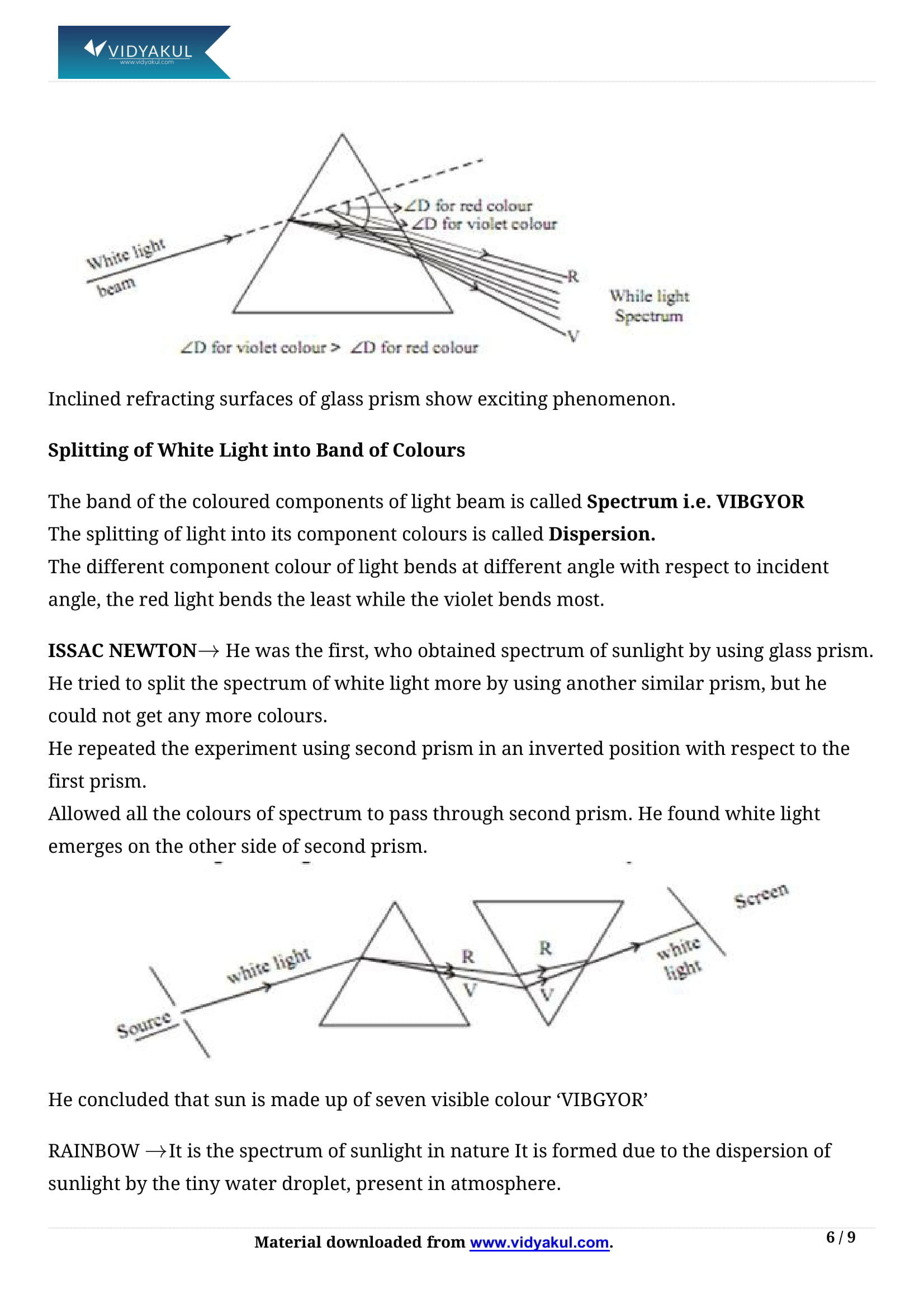
A prism splits the incident white light into a band of seven colours. The band of the coloured components of a light beam is called its spectrum. Isaac Newton was the first to use a glass prism to obtain the sunlight spectrum. Different colours of light bend through different angles with respect to the incident ray, as they pass through a prism. The red light bends the least while the violet the most. Thus the rays of each colour emerge along different paths and thus become distinct.
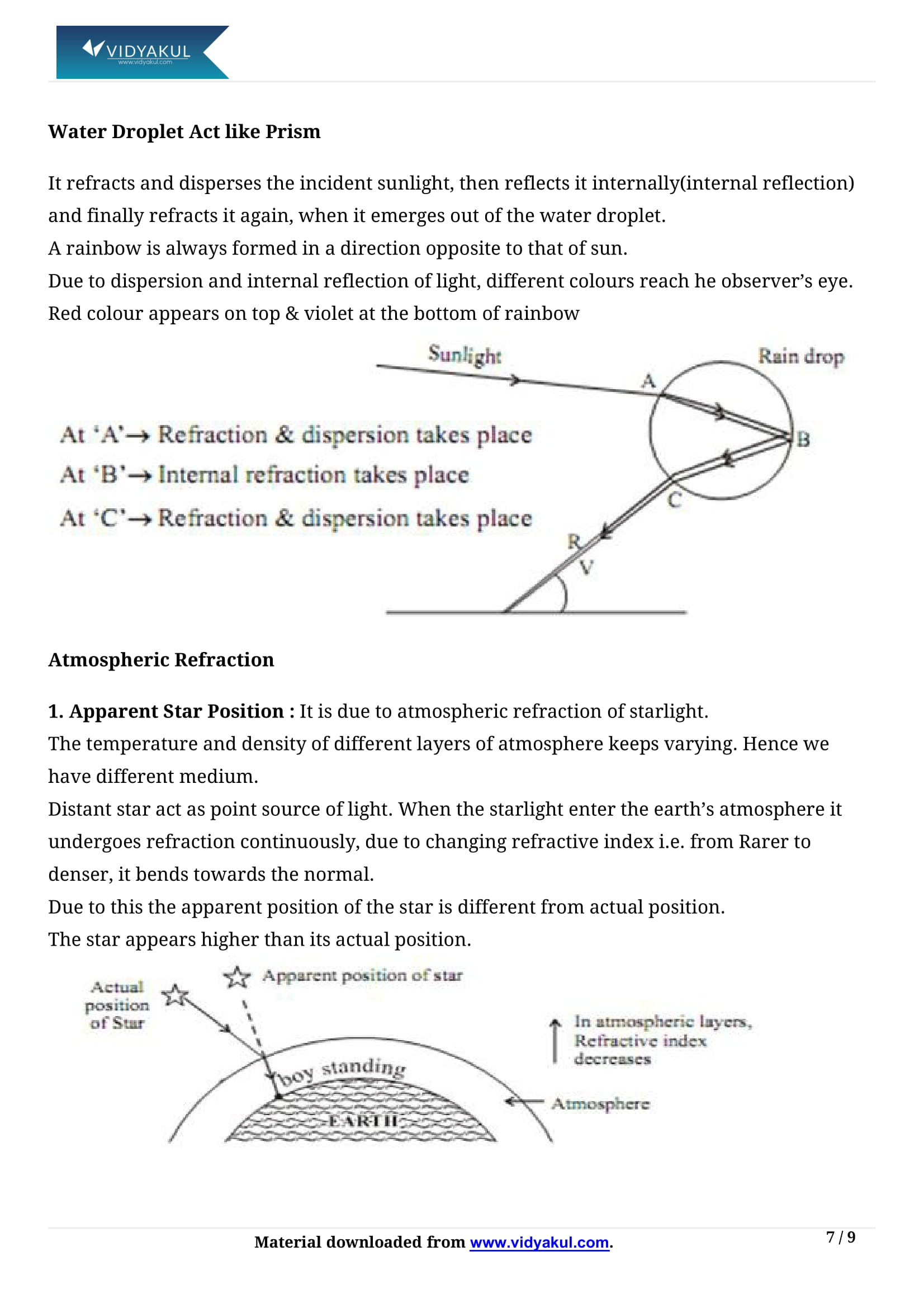
The refraction of light by the Earth’s atmosphere is known as atmospheric refraction. Atmospheric refraction is caused by the bending of light rays when they pass through the layers of the earth’s atmosphere, which are of different optical densities.
The twinkling effect of stars is due to the atmospheric refraction of starlight. The starlight undergoes continuos refraction as it passes through the atmosphere before it reaches earth. As the path of rays of light coming from the star goes on varying slightly, the apparent position of the star fluctuates and the amount of starlight entering the eye flickers.
When a light beam goes through a medium, it hits the particles existing in them. Due to this phenomenon, some of the light rays get absorbed while a few get scattered in various directions. The intensity of the scattered light rays depends on the particles’ size and wavelength.
Topics and Sub-topics
NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 11: The Human Eye and its Colorful World helps students understand the structure and various defects of the human eye. Students also learn corrective actions to correct these visual defects. The concept of light dispersion is well explained in easy-to-understand language so that students can easily understand it. Sunrise and sunset events are also covered in this chapter strictly in accordance with the stipulated program and CBSE recommendations.
Below-mentioned is the list of topics present in Class 10 Science Chapter 11:
Few Important Questions
If Ram is facing west and he sees a rainbow in front of him then, in which direction most probably the Sun is?
The Sun and the rainbow will always be in opposite directions. A Rainbow is formed when a raindrop causes the light from the Sun to undergo partial internal reflection. This means that the light is reflected back in the direction it came from (from the Sun). Hence, we can see a rainbow only if our back is facing the Sun. Hence, in this case, the Sun will be in the east direction.
Which colour will be refracted the most when white light is dispersed from a prism?
The refractive index of the medium is maximum for the violet light and minimum for the red light. Therefore, when white light enters a prism, it disperses into seven constituent colours and violet light shows the maximum deviation.
Why one cannot see through fog?
Fog is a visible aerosol consisting of tiny water droplets or ice crystals that remain near the surface of the earth. When light travels through the fog, it interacts with the water droplets of the fog and is scattered by them. The scattering of light by fog droplets is not uniform in all directions. The light from various objects gets scattered by water droplets, so the eye cannot distinguish the objects, and thus one cannot see through the fog.
Of all the sense organs, the human eye is the most significant one as it enables us to see the beautiful, colourful world around us. The eye is spherical in shape and has a diameter of 2.3 cm on average. The internal structure of the eye includes- the cornea, iris, pupil, lens, ciliary muscles, retina, nerve cells, optic nerve, yellow spot, aqueous and vitreous humor, and suspensory ligament.
Myopia – This is also called as the short-sightedness. A person with this eye defect can only see the nearby objects clearly compared to distant objects. This condition can be corrected using a concave lens.
Hypermetropia – This is also called as the farsightedness. A person with this eye defect can only see the distant objects clearly compared to near objects. This condition can be corrected using a convex lens.
Presbyopia – This is an age-related condition caused due to the weakening of ciliary muscles, hardening of the lens, and reduced lens flexibility. A person with this defect usually finds difficulties to focus on nearby objects unable to read or write.
Cataract – This is an age-related condition caused due to the loss of transparency of the lens by erosion of lens proteins. It usually results in blurry vision, cloudy lenses and can be corrected by replacing the old lens with an artificial lens.
A prism splits the incident white light into a band of seven colours. The band of the coloured components of a light beam is called its spectrum. Isaac Newton was the first to use a glass prism to obtain the sunlight spectrum. Different colours of light bend through different angles with respect to the incident ray, as they pass through a prism. The red light bends the least while the violet the most. Thus the rays of each colour emerge along different paths and thus become distinct.
The refraction of light by the Earth’s atmosphere is known as atmospheric refraction. Atmospheric refraction is caused by the bending of light rays when they pass through the layers of the earth’s atmosphere, which are of different optical densities.
The twinkling effect of stars is due to the atmospheric refraction of starlight. The starlight undergoes continuos refraction as it passes through the atmosphere before it reaches earth. As the path of rays of light coming from the star goes on varying slightly, the apparent position of the star fluctuates and the amount of starlight entering the eye flickers.
When a light beam goes through a medium, it hits the particles existing in them. Due to this phenomenon, some of the light rays get absorbed while a few get scattered in various directions. The intensity of the scattered light rays depends on the particles’ size and wavelength.
If Ram is facing west and he sees a rainbow in front of him then, in which direction most probably the Sun is?
Which colour will be refracted the most when white light is dispersed from a prism?
Why one cannot see through fog?
Learn More about the same in Human Eye and Colourful World Class 10 Notes PDF.
Download Latest Class 10 Sample Papers 2019 for Board Exams
- CBSE Class 10 Sample Papers 2019 PDF
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Sample Papers 2019 PDF
- CBSE Class 10 Science Sample Papers 2019 PDF
- CBSE Class 10 English Sample Papers 2019 PDF
- CBSE Class 10 Hindi Sample Paper 2019 PDF
- CBSE Class 10 Social Studies Sample Papers 2019 PDF
Download this solution for FREE Download this PDF
Download Vidyakul App for more Important notes, PDF's and Free video lectures.