Cell Cycle and Cell Division Class 11 Notes

Chapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell Division
CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 10 covers the concepts of the cell cycle and cell division. This chapter is primarily about how cycles of growth and division allow one cell to form millions of cellular structures. The NCERT notes for Class 11 Biology Chapter 10 is a great resource for GCSEs and is based on the latest CBSE syllabus.
Vidyakul subject matter experts provide NCERT notes for Chapter 10 of CBSE Class 11 Biology. Students can use the NCERT Class 11 Biology notes anytime online at Vidyakul. In addition to NCERT notes, Vidyakul provides over 100 free exercises on cell cycle, mitosis, and meiosis based on 53 general concepts. Visit Vidyakul for more information.
CBSE CLASS 11 BIOLOGY CH-10
Points to Remember
Below are some important points to remember from the NCERT notes for Class 11 Biology Chapter 10 :
Rudolf Virchow (1858) gave cell lineage theory stating ‘Omnis cellula e cellula’, which means that cells arise from pre-existing cells.
All living organisms are composed of cells, and all cells arise from other cells.
The process by which cells multiply is called cell division.
Any sexually reproducing organism starts its life cycle from a single-celled zygote.
Cell division does not stop with the formation of the mature organism but continues throughout its life cycle.
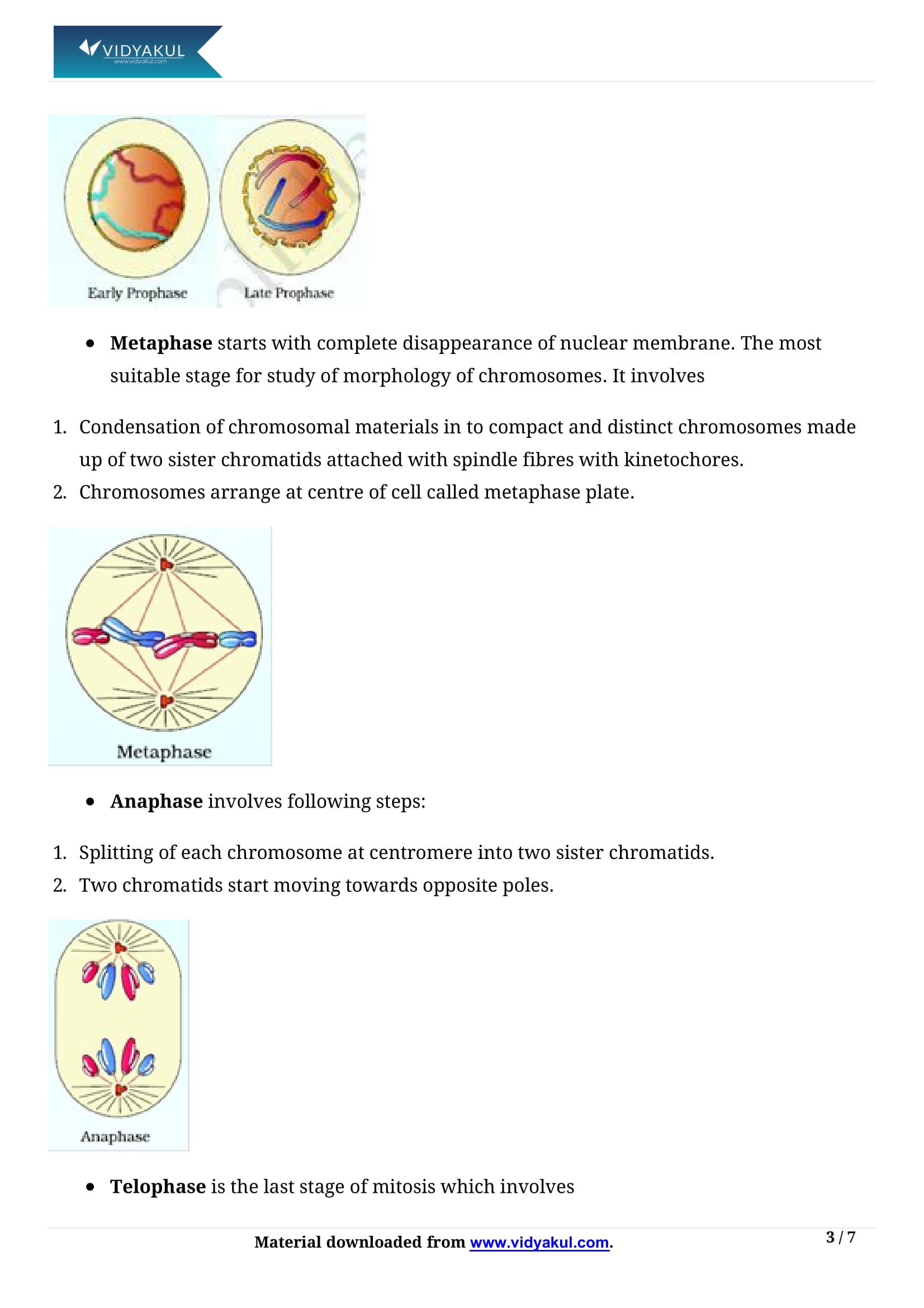
Mitosis consists of four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.
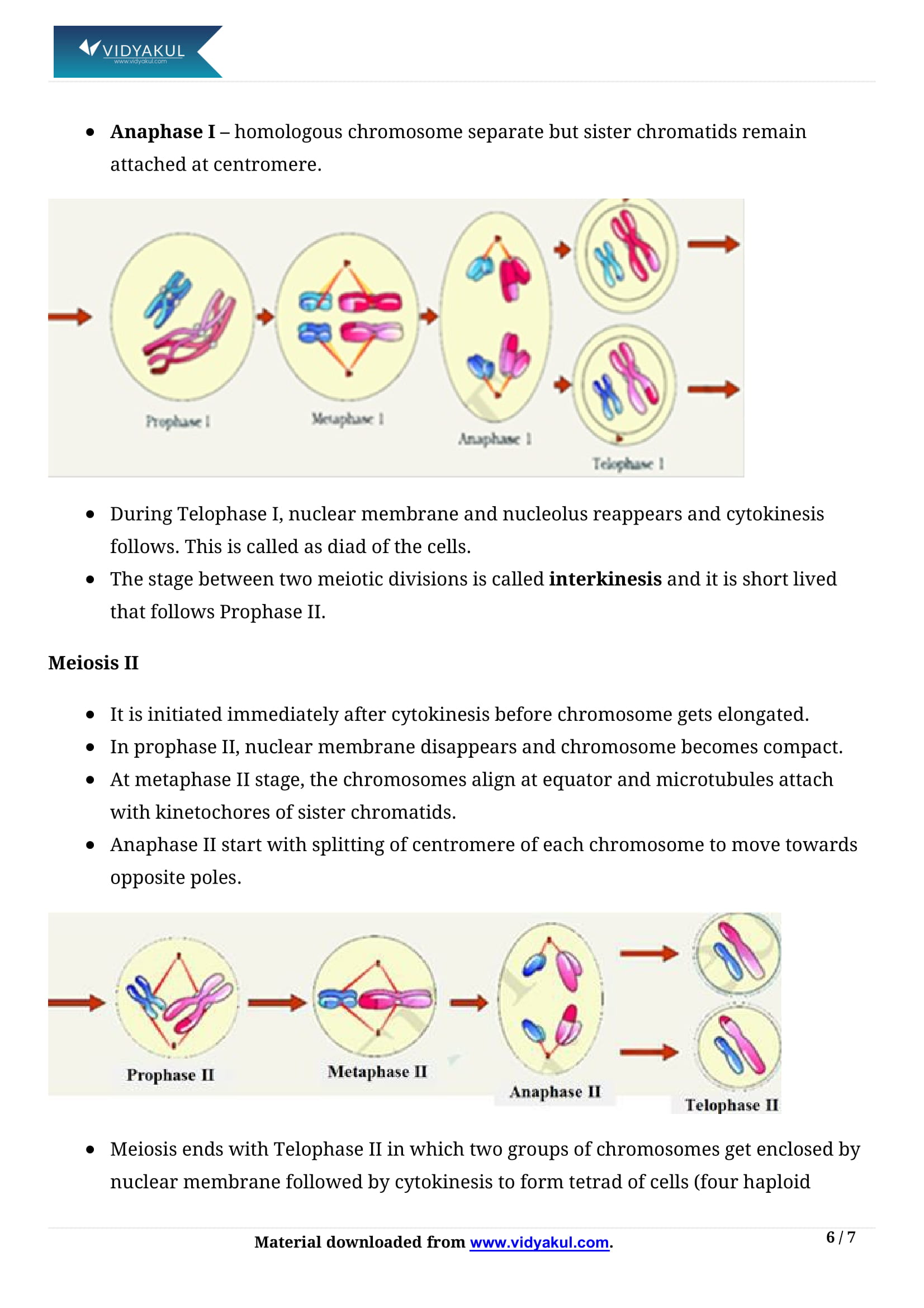
In contrast to mitosis, meiosis occurs in the diploid cells destined to form gametes.
Meiosis is the reduction division since it reduces the chromosome number by half while making the gametes.
Topics and Sub-topics
Chapter 10, “Biology,” explains in detail what the cell cycle is, its stages, mitosis, meiosis, and their importance. After reading this chapter, students should be able to describe how cell entities are created and the step-by-step processes involved. Students can refer to Vidyakul's NCERT Class 11 Biology book for Chapter 10 to reinforce their conceptual understanding in the chapters.
In addition to the book, students can expand their knowledge using the Vidyakul NCERT notes. NCERT Class 11 notes Biology helps students understand concepts easily. Students can practice free questions provided on Vidyakul. This way students can practice and take free mock tests. Vidyakul has the best prep tips to help students. Additionally, students should focus on the NCERT notes that benefit them. Vidyakul also makes learning fun for students.
Let us look at the topics that students are going to study in this chapter:
Frequently Asked Questions
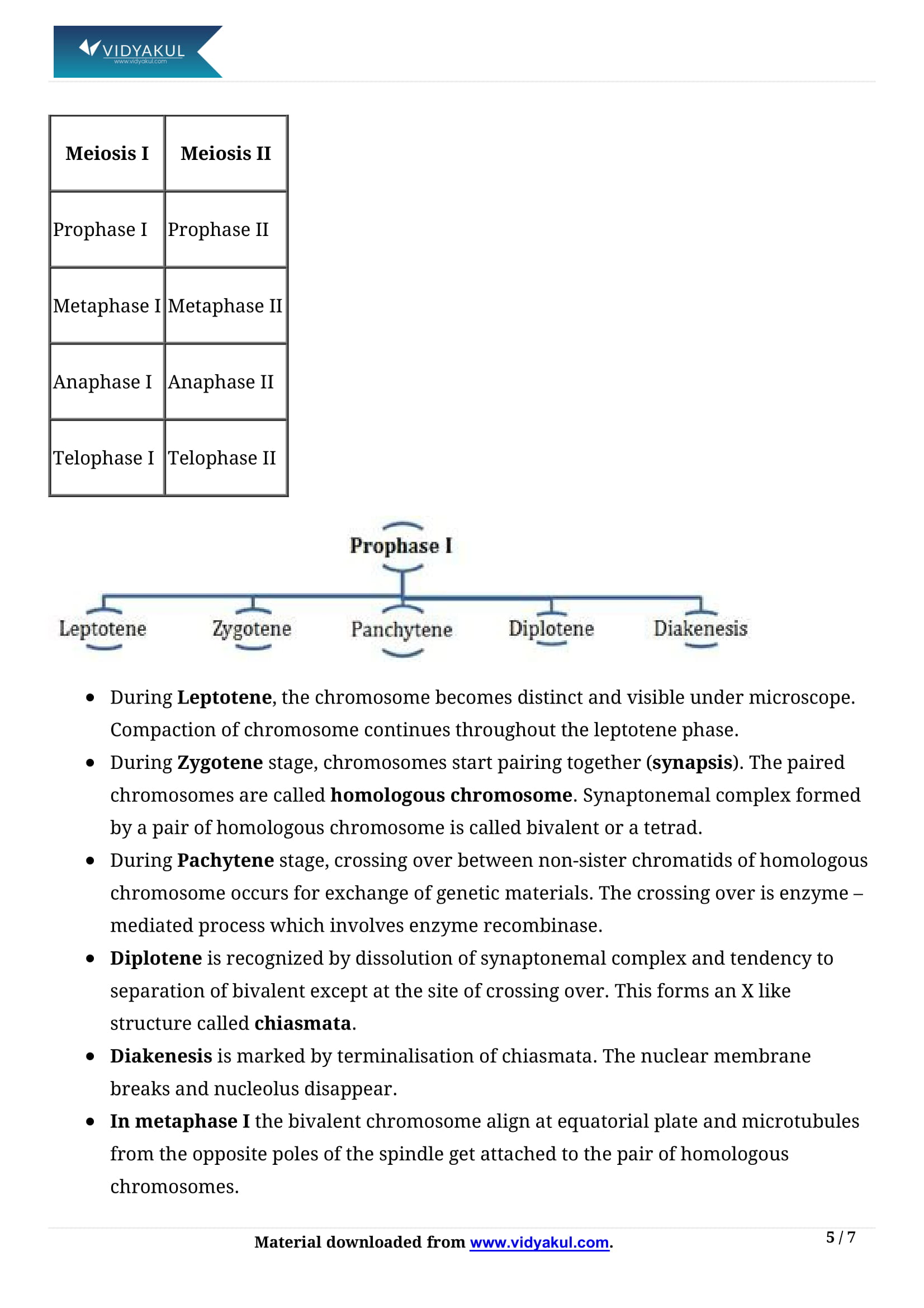
Describe the different phases of meiotic prophase – I. Mention the chromosomal events during each stage.
During the prophase – I, genetic recombination and variation in sexually reproducing entities takes place due to the events of this stage.
Leptotene
Chromosomes are long, thin and slender
Chromatin network exposes and threads appear clear
The diploid number of chromosomes
Zygotene
Similar chromosomes turn intimately associated
Synapse is exact hence pairing is not just between chromosomes, but corresponding individual units.
Chromosomes appear thicker and shorter
Pachynema
Synaptic chromosomes become intimately related
Thick and short pair of chromosomes
Cross over occurs, Chiasmata visible clearly
Diplotene
Homologous chromosomes start detaching from each other.
Chiasmata tends to shift away from chromosomes, termed as thermalization of chiasmata
Chromosomes detach out, but it is an incomplete separation
Nucleolus and nuclear membrane start to fade.
Diakinesis
The bivalents are randomly distributed after further condensation
The paired chromosomes separate completely
Terminalisation of chiasmata is almost concluded
The disappearance of the nucleolus and nuclear membrane
State differences between the events of meiosis and mitosis.
Following are the differences :
Explain:
a) Synaptonemal complex
b) Metaphase plate
a) These are zipped-structures that are assembled during the prophase of the meiosis – I between homologous chromosomes. This disassembly and assembly is interlinked with the continuous rearrangements of the chromatin during the meiotic prophase such as the poring, recombination, condensation, and dysfunction of homologous chromosomes. These regulate the number and distribution of reciprocal exchanges between the homologous chromosomes. They convert cross over to functional chiasmata.
b) The centromeres of the chromosomes in the metaphase gather on the metaphase plate which is an imaginary line at an equal distance from the two centrosome poles. The alignment is even due to the opposite kinetochore microtubules. The chromosomes at this plate, the sister chromatids, in particular, are connected to the package of four to eight spindle fibres.
Write the phases of the cell cycle against each of the events
a) The disintegration of the nuclear membrane
b) The appearance of the nucleolus
c) Division of centromere
d) Replication of DNA
a) Prophase.
b) Telophase.
c) Anaphase.
d) S-phase.
Practice Questions
How does cytokinesis in plant cells differ from that in animal cells?
Telophase is the reverse of prophase. Elucidate the statement.
Which is the cell that is captured in the diplotene phase for months and years? How does it complete its cell cycle?
A cell having 32 chromosomes undergoes mitotic division. During metaphase, what will the chromosome number (N) of the cell? During anaphase, what will the DNA content of the cell be?
How much time will two E. Coli cells take to become 32 cells if the average duplication time of E. coil is 20 minutes?
Rudolf Virchow (1858) gave cell lineage theory stating ‘Omnis cellula e cellula’, which means that cells arise from pre-existing cells.
All living organisms are composed of cells, and all cells arise from other cells.
The process by which cells multiply is called cell division.
Any sexually reproducing organism starts its life cycle from a single-celled zygote.
Cell division does not stop with the formation of the mature organism but continues throughout its life cycle.
Mitosis consists of four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.
In contrast to mitosis, meiosis occurs in the diploid cells destined to form gametes.
Meiosis is the reduction division since it reduces the chromosome number by half while making the gametes.
Describe the different phases of meiotic prophase – I. Mention the chromosomal events during each stage.
Chromosomes are long, thin and slender
Chromatin network exposes and threads appear clear
The diploid number of chromosomes
Similar chromosomes turn intimately associated
Synapse is exact hence pairing is not just between chromosomes, but corresponding individual units.
Chromosomes appear thicker and shorter
Synaptic chromosomes become intimately related
Thick and short pair of chromosomes
Cross over occurs, Chiasmata visible clearly
Homologous chromosomes start detaching from each other.
Chiasmata tends to shift away from chromosomes, termed as thermalization of chiasmata
Chromosomes detach out, but it is an incomplete separation
Nucleolus and nuclear membrane start to fade.
The bivalents are randomly distributed after further condensation
The paired chromosomes separate completely
Terminalisation of chiasmata is almost concluded
The disappearance of the nucleolus and nuclear membrane
State differences between the events of meiosis and mitosis.
Explain:
Write the phases of the cell cycle against each of the events
How does cytokinesis in plant cells differ from that in animal cells?
Telophase is the reverse of prophase. Elucidate the statement.
Which is the cell that is captured in the diplotene phase for months and years? How does it complete its cell cycle?
A cell having 32 chromosomes undergoes mitotic division. During metaphase, what will the chromosome number (N) of the cell? During anaphase, what will the DNA content of the cell be?
How much time will two E. Coli cells take to become 32 cells if the average duplication time of E. coil is 20 minutes?
Learn more about the same in Cell Cycle and Cell Division Class 11 Notes pdf.
Download this solution for FREE Download this PDF
Download Vidyakul App for more Important videos, PDF's and Free video lectures.