Plant Growth and Development Class 11 Notes

Chapter 15 Plant Growth and Development
Plant Growth and Development Class 11 NCERT notes can be easily found on this page. The notes proposed here have been developed by Vidyakul academic experts, primarily based on NCERT textbooks. Notes are provided in order with schematic drawings where applicable. This makes it easier for learners to follow and get the most out of it.
CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 15 covers growth stages, growth rates, growth conditions, plant growth regulators, and photoperiod. Students must practice all the in-text questions provided by Vidyakul to achieve the best marks in the exam. Keep reading the article to know NCERT notes for Class Class 11 Biology Chapter 15.
CBSE CLASS 11 BIOLOGY CH-15
Points to Remember
Some of the important points to be remembered from NCERT Class 11 Biology Chapter 15 have been mentioned below:
Growth is one of the most conspicuous events in any living organism.
It is an irreversible increase that can be expressed in terms of size, area, length, height, weight, etc.
It conspicuously involves increased protoplasmic material.
Root and shoot apical meristems, sometimes along with intercalary meristem, contribute to the growth of plants.
Growth in plants is indeterminate as plants retain the capacity for unlimited growth throughout their life.
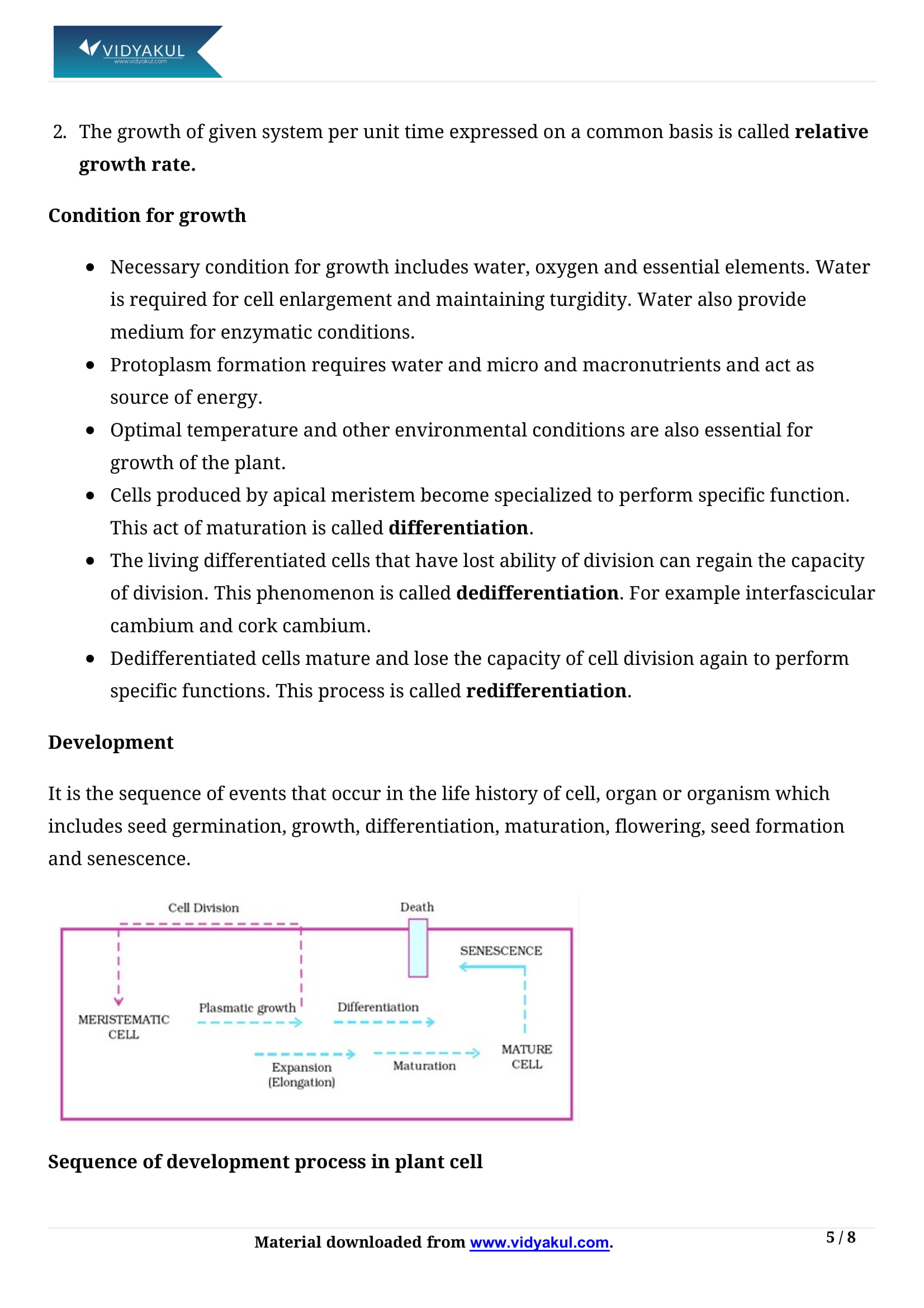
When a cell loses the capacity to divide, it leads to differentiation that results in the development of structures that is commensurate with the function the cells finally have to perform.
A differentiated cell may dedifferentiate and then redifferentiate.
Plants exhibit plasticity in development, i.e., the same organ may show different kinds of structures in different phases of life or in different habitats.
Plant growth and development are under the control of both intrinsic and extrinsic factors.
Plant growth regulators (PGRsPGRs) are organic molecules of diverse chemical composition which are synthesized in one part of the plant body and transported to another part where they are active.
Plant growth and development is also affected by light, temperature, nutrition, oxygen status, gravity and such external factors.
The growth hormones are translocated through different tissues, e.g., auxins through parenchyma, GAS and ABA mainly through phloem and cytokinins through the xylem.
Ethylene is a gaseous hormone and is readily absorbed and transported within the plant body.
There are two kinds of flowering stimuli, a hormone called florigen and another is proteinaceous pigment known as phytochrome.
Topics and Sub-topics
Chapter 15, Plant Growth and Development, teaches the students about the basics, such as various phases of growth, different plant growth regulators and other important topics that students will face during their higher grades. Students must explore and find out answers to as many questions as possible to become efficient in the subject.
Below-mentioned is the list of topics present in Class 11 Biology Chapter 15.
Frequently Asked Questions
Winter varieties, when planted in spring, do not produce flowers or mature grains within the span of a flowering season. Explain.
In some plants, flowering is either qualitatively or quantitatively reliant on subjection to lower temperatures, the process is referred to as vernalization. This limits advanced reproductive development rate in maturing season thereby allowing them to have enough time to gain maturity. Vernalisation promotes flowering by a span of low temperatures. Some plants like wheat, barley have two types of varieties – spring and winter varieties. The spring variety is planted in the spring and flowers, producing grains towards the termination of the growing season. While the winter varieties, when planted in spring fail to flower or generate mature grains within the flowering season, this is why they are planted in autumn. Over winter, they germinate and turn out as small seedlings, restarting development in the spring and are gathered in mid-summer.
Several variations of wheat are cultivated in autumn and harvested in the next midsummer.
a) Give reason
b) What is the flowering in lower temperatures referred to as?
c) Name the plant hormone that can substitute for the cold treatment.
a) If planted in spring, winter varieties do not flower or generate mature grains in a span of the flowering season, hence they are cultivated in autumn. Over winter, they sprout and come out as tiny seedlings, resuming growth in the spring and are collected in mid-summer.
b) Vernalisation.
c) Gibberellin.
List a hormone that:
a) Is in nature, gaseous.
b) Is in charge of phototropism.
c) Influences femaleness in cucumber flowers.
d) Is utilized to kill weeds(dicots).
e) In long-day plants, induces flowering.
a) Ethylene(C2H4)
b) Auxin.
c) Ethylene(C2H4).
d) Auxin.
e) Gibberellin.
Practice Questions
Write the structural features of
a) Meristematic cells near the root tip
b) The cells in the elongation zone of the root
Is there a difference in the growth pattern of plants and animals? QDo all parts of the plant grow endlessly? List the regions of the plant that can grow endlessly, if no.
Explain the following with examples from various plant tissues
a) Differentiation
b) De-differentiation
c) Redifferentiation
Why is it difficult to designate any effect to a single hormone during experimentation?
Where are plant hormones formed? How are the hormones passed to the specific site of activity?
What are Plant growth regulators?
Which plant hormone is used to manipulate and stimulate the maturation of sugarcane crop?
What are the functions of Auxins in plant growth?
Growth is one of the most conspicuous events in any living organism.
It is an irreversible increase that can be expressed in terms of size, area, length, height, weight, etc.
It conspicuously involves increased protoplasmic material.
Root and shoot apical meristems, sometimes along with intercalary meristem, contribute to the growth of plants.
Growth in plants is indeterminate as plants retain the capacity for unlimited growth throughout their life.
When a cell loses the capacity to divide, it leads to differentiation that results in the development of structures that is commensurate with the function the cells finally have to perform.
A differentiated cell may dedifferentiate and then redifferentiate.
Plants exhibit plasticity in development, i.e., the same organ may show different kinds of structures in different phases of life or in different habitats.
Plant growth and development are under the control of both intrinsic and extrinsic factors.
Plant growth regulators (PGRsPGRs) are organic molecules of diverse chemical composition which are synthesized in one part of the plant body and transported to another part where they are active.
Plant growth and development is also affected by light, temperature, nutrition, oxygen status, gravity and such external factors.
The growth hormones are translocated through different tissues, e.g., auxins through parenchyma, GAS and ABA mainly through phloem and cytokinins through the xylem.
Ethylene is a gaseous hormone and is readily absorbed and transported within the plant body.
There are two kinds of flowering stimuli, a hormone called florigen and another is proteinaceous pigment known as phytochrome.
Winter varieties, when planted in spring, do not produce flowers or mature grains within the span of a flowering season. Explain.
List a hormone that:
Write the structural features of
Is there a difference in the growth pattern of plants and animals? QDo all parts of the plant grow endlessly? List the regions of the plant that can grow endlessly, if no.
Explain the following with examples from various plant tissues
Why is it difficult to designate any effect to a single hormone during experimentation?
Where are plant hormones formed? How are the hormones passed to the specific site of activity?
What are Plant growth regulators?
Which plant hormone is used to manipulate and stimulate the maturation of sugarcane crop?
What are the functions of Auxins in plant growth?
Learn more about the mean, median and mode in Plant Growth and Development Class 11 Notes pdf.
Download this solution for FREE Download this PDF
Download Vidyakul App for more Important videos, PDF's and Free video lectures.