Breathing and Exchange of Gases Class 11 Notes

Chapter 17 Breathing and Exchange of Gases Notes
This article provides students with detailed NCERT notes for Chapters 11 and 17 of Biology, Respiration and Gas Exchange. Top scholars and educators determine all NCERT notes available here at Vidyakul. The NCERT class 11 biological notes presented here are accurate and updated. All the questions in the text and at the end of the chapters, and detailed answers to each question, can be found here.
Students should read this article about the NCERT notes for Year 11 Biology Chapter 17. Chapters consist of 6 main themes and various sub-themes. Students can start practicing questions to master the concepts. It also helps in quick and last minute revisions of chapters for all tests.
CBSE CLASS 11 BIOLOGY CH-17
Points to Remember
Below we have summarised some of the important points to remember for Class 11 Biology Chapter 17. Students can refer to them while studying.
The respiratory system allows the exchange of respiratory gases between the environment and the blood.
The recording of breathing is termed as spirogram.
Oxygen does not dissolve easily in water; only 1.5% of the 02 is dissolved in blood plasma.
Carbon monoxide has 200-250 times more affinity for haemoglobin as compared to oxygen.
The number of RBCs per unit volume of blood is likely to be higher in a person living at a higher altitude because air is less dense.
Topics and Sub-topics
This article section lists the important topics covered in Chapter 17 – Breathing and Exchange of Gases. This chapter talks about the mechanisms of breathing and respiration in animals. Students will most likely enjoy this chapter.
The NCERT notes for Breathing and Exchange of Gases has numerous important topics and sub-topics listed in the table below. Practicing the question from every topic is important to grasp the concept. This way, students can also test their level of understanding through Vidyakul’s mock test, which they can customise according to their level.
Frequently Asked Questions
Write a note on the mechanism of breathing.
a) Inspiration – It is inducted by the diaphragm contraction that raises the volume of the thoracic chamber in the anteroposterior axis. The inter-costal muscles contracts causing external protrusion of the sternum and ribs resulting in an increment in the volume of the thoracic chamber in the dorsoventral axis. This increase in the thoracic volume results in a similar increase in pulmonary volume causing reduced intrapulmonary pressure to lesser than the atmospheric pressure which results in inspiration.
b) Expiration – The inter-costal muscles reverse the sternum and diaphragm to their original positions with the diaphragm relaxing, which decreases the thoracic volume and hence the pulmonary volume. Expulsion of air occurs as the intra-pulmonary pressure increases to a level somewhat above the atmospheric pressure causing expiration.
Describe the role of the neural system in controlling respiration.
The neural system maintains and moderates the respiratory rhythm as per the demands of the body tissues. The respiratory rhythm centre present in the brain is responsible for regulation. The pneumotaxic centre, another region in the pons of the brain, moderates the functions of the respiratory rhythm centre. The neural signals from this centre have the ability to reduce the duration of inspiration hence altering the rate of respiration. A chemosensitive area present adjacent to the rhythm centre is very sensitive to hydrogen ions and CO2 which activate this centre by an increase of these substances. These send down a signal to the rhythm centre to cause essential adjustments in the process which can cause the elimination of these substances. Changes in CO2 and hydrogen ions are recognized by receptors linked with aortic arch and carotid artery, thereby sending signals for corrective actions to the rhythm centre
State the differences between the following:
a) Expiratory and inspiratory reserve volume
b) Total lung capacity and vital capacity
c) Occupational respiratory disorder and Emphysema
The differences are as follows:
a)
b)
c)
List the following steps in a sequential manner for the completion of the respiration process.
a) Diffusion of oxygen and CO2 across the alveolar membrane
b) Transportation of gases by blood
c) Utilization of oxygen for catabolic reactions by the cells and hence the resultant release of CO2
d) Pulmonary ventilation through which atmospheric air is drawn in and carbon dioxide-rich alveolar air is given out
e) Diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide between tissues and blood
a) Diffusion of oxygen and CO2 across the alveolar membrane
b) Transportation of gases by blood
e) Diffusion of oxygen and CO2 between tissues and blood
c) Utilization of oxygen for catabolic reactions by the cells and hence the resultant release of CO2
d) Pulmonary ventilation through which atmospheric air is drawn in and carbon dioxide-rich alveolar air is given out
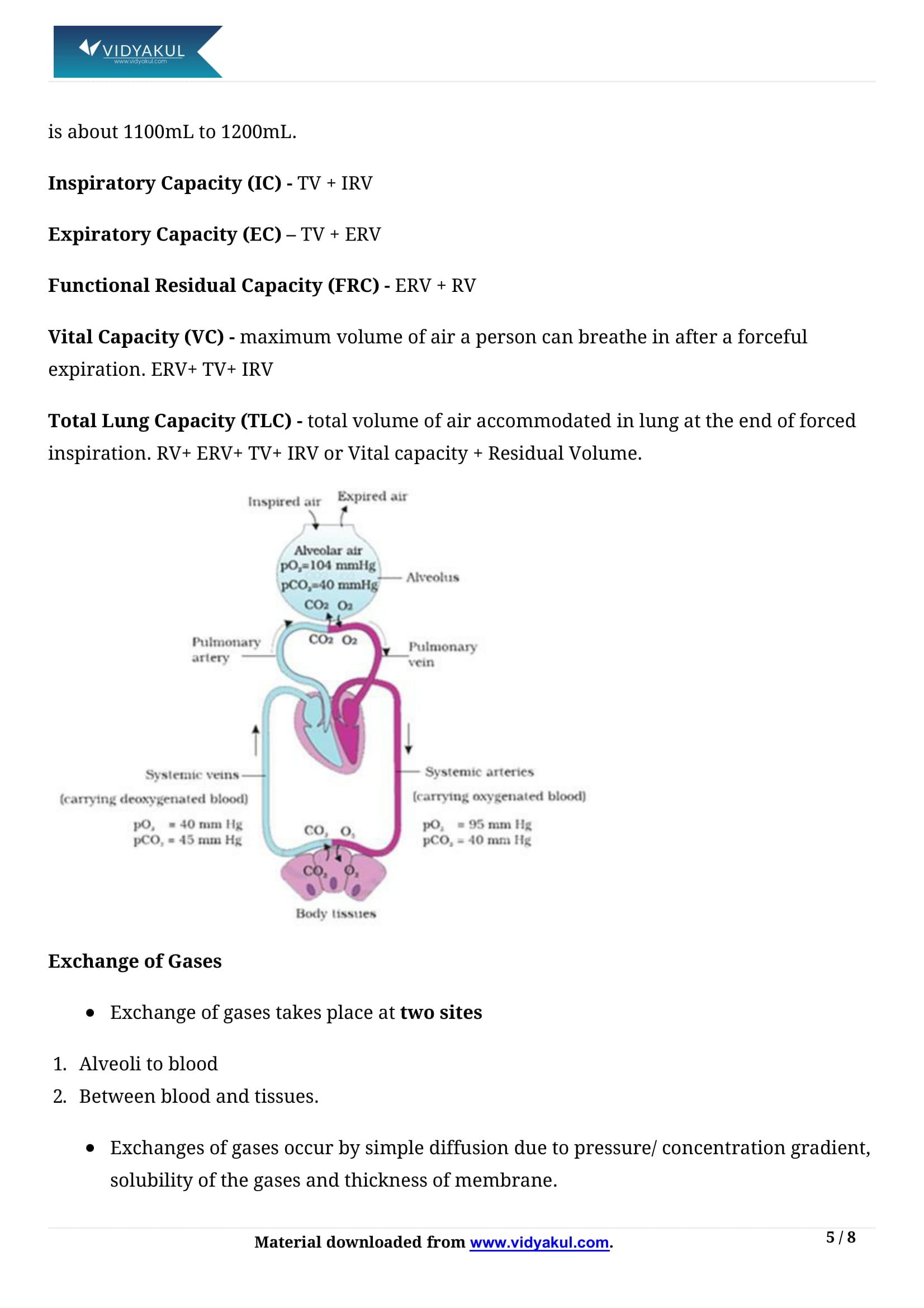
Write the various modes of transportation of carbon dioxide in the blood.
It is carried in the blood in three forms:
Dissolved state under normal pressure and temperature, 7% of CO2 is transported by physical solution
As carbamino compounds, carbon dioxide directly combines with Hb to form an unstable compound, the carbamino compounds
As bicarbonate ions
Explain why the diffusion of carbon dioxide by the diffusion membrane per unit difference in partial pressure is much greater compared to oxygen.
The solubility rate of CO2 is 22-25 times more than oxygen.
Practice Questions
Write the name and important function of the fluid-filled double membranous layer surrounding the lungs.
Which is the prime site for the exchange of gases in our body?
Why does smoking cigarette cause emphysema?
Organize the following in ascending order
a) Tidal volume
b) Residual volume
c) Inspiratory reserve volume
d) Expiratory capacity
Write the organs of respiration in the entities given below:
a) Flatworm
b) Frog
c) Birds
d) Cockroach
The respiratory system allows the exchange of respiratory gases between the environment and the blood.
The recording of breathing is termed as spirogram.
Oxygen does not dissolve easily in water; only 1.5% of the 02 is dissolved in blood plasma.
Carbon monoxide has 200-250 times more affinity for haemoglobin as compared to oxygen.
The number of RBCs per unit volume of blood is likely to be higher in a person living at a higher altitude because air is less dense.
Write a note on the mechanism of breathing.
Describe the role of the neural system in controlling respiration.
State the differences between the following:
List the following steps in a sequential manner for the completion of the respiration process.
Dissolved state under normal pressure and temperature, 7% of CO2 is transported by physical solution
As carbamino compounds, carbon dioxide directly combines with Hb to form an unstable compound, the carbamino compounds
As bicarbonate ions
Explain why the diffusion of carbon dioxide by the diffusion membrane per unit difference in partial pressure is much greater compared to oxygen.
Write the name and important function of the fluid-filled double membranous layer surrounding the lungs.
Which is the prime site for the exchange of gases in our body?
Why does smoking cigarette cause emphysema?
Organize the following in ascending order
Write the organs of respiration in the entities given below:
Learn more about it in Breathing and Exchange of Gases Class 11 Notes pdf.
Download this solution for FREE Download this PDF
Download Vidyakul App for more videos, PDF's and Free video lectures.