Chemical Coordination and integration Class 11 Notes

Chapter 22 Chemical Coordination and integration
If a student is looking for an NCERT notes for class 11 chemical coordination and integration, this article may be helpful. It gives them a detailed NCERT notes for Chapter 22 of Grade 11 Biology. The notes is consistent with the NCERT textbook. Prepared by Vidyakul's subject matter experts and presented here in a structured manner.
Class 11 Biology Chapter 22 discusses animal hormones, endocrine glands and hormones, mechanisms of action of hormones, pituitary gland, thyroxine and related disorders. Students are expected to follow all questions and answers provided in the text.
CBSE CLASS 11 BIOLOGY CH-22
Points to Remember
Below mentioned are some of the important points of the Class 11 Biology Chemical Coordination and Integration chapter.
Endocrine Glands and Hormones: (i) There are two coordinating, integrating and interdependent systems in our body, namely the nervous system and endocrine system.
(ii) The endocrine system achieves coordination and integration by transmitting information through hormones also known as chemical messengers.
(iii) Endocrinology is the study of endocrine glands and hormones.
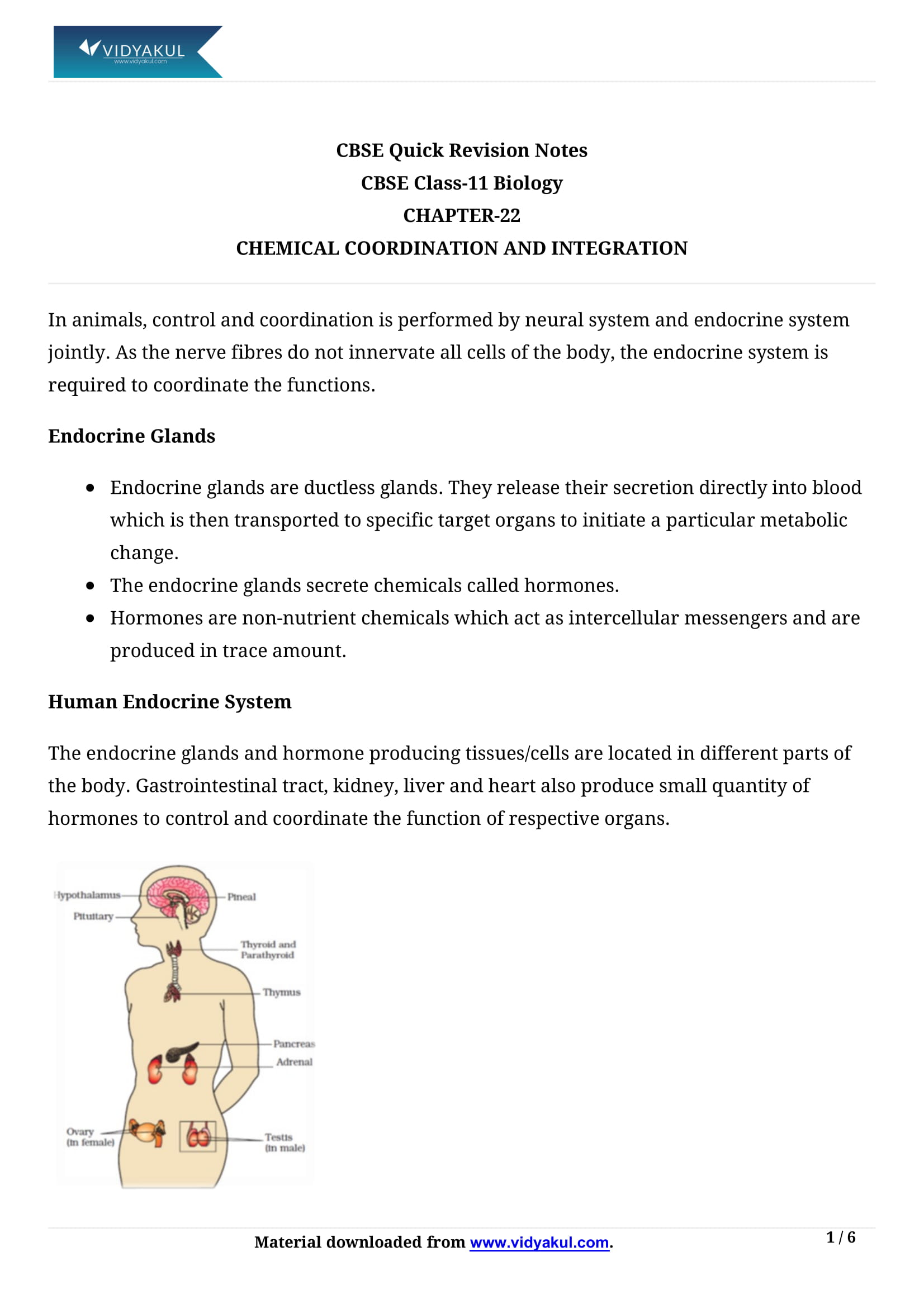
(iv) The term hormone was coined by Starling in 19051905. The endocrine system consists of hypothalamus, pituitary, pineal, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pancreas, thymus and gonads (testis and ovary).
(v) Some other organs, e.g., gastrointestinal tract, kidney, heart, etc., also produce hormones.
(vi) Prostaglandins are long chain unsaturated fatty acids which regulate vasoconstriction, vasodilation, contraction of uterine muscles, etc.
(vii) Pheromones are molecules used for chemical communication between individual animals.
Thyroid Gland: (i) The thyroid gland hormones play an important role in the regulation of the basal metabolic rate, development and maturation of the central neural system, erythropoiesis, metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and fats, menstrual cycle.
(ii) Another thyroid hormone, i.e., thyrocalcitonin secreted by C-cells regulates calcium levels in our blood by decreasing it.
Topics and Sub-topics
Class 11 Biology Chapter 22 teaches crucial aspects of the human body and its hormones. Students will find the concepts interesting to understand. Once the conceptual videos at Vidyakul are followed, it becomes easy for the students to find answers to all the questions. Students are advised to answer as many questions as possible to become proficient in the topic.
Vidyakul provides notes to all the questions of the Chapter 11 textbook, considering the latest syllabus. At Vidyakul, students can practice all the questions for free. We have provided the list of topics present in Class 11 Biology chapter 22 below:
Frequently Asked Questions
A milkman’s cow refuses to give milk. On being fondled by the calf, the cow produced enough milk. Explain the significance of the endocrine gland and the pathway related to this response.
A neuroendocrine reflex is created when calf suckling occurs that causes an increase in the oxytocin from the neurohypophysis. In the hypothalamus, oxytocin is synthesized in specific nuclei, the paraventricular nucleus, and the supraoptic nucleus. Here the neurons produce the oxytocin precursor and bundle it into vesicles. The level of oxytocin in the blood gets concentrated within a minute or two after the stimulation which causes smooth muscle contraction of the udder causing milk to flow. An intra-udder hormone that functions like oxytocin would do a similar function. Following is a summarization. Suckling stimulus → Hypothalamus → Neurohypophysis → Oxytocin → Udder → Flow of milk.
A urine sample contained increased content of glucose and ketone bodies. Answer the questions below basis this observation.
a) Name the hormone and gland associated with this condition.
b) On which cells do these hormones act?
c) Name the condition. How can it be rectified?
a) Insulin hormone and Insulin gland. b) It acts on the β-cells of islets of Langerhans present in the pancreas c) Prolonged hyperglycemia causes diabetes mellitus that is linked to loss of glucose via urine and accumulation of harmful compounds called ketone bodies. Insulin therapy can be successfully used to treat Diabetic patients.
Describe the importance of hormones and endocrine glands responsible for regulating the Calcium Homeostasis.
The hormones and endocrine glands that regulate calcium homeostasis are thyroid and parathyroid glands and their related hormones which are Parathyroid hormone (PTH) and calcitonin. The endoderm of the embryo develops the parathyroid glands and has two types of cells – oxyphil cells and chief cells. The chief cells secrete the parathyroid hormone(PTH) which is involved in controlling phosphate and calcium stability between other tissues and blood. From bones, it causes the secretion of calcium into the blood. PTH causes an increase in the reabsorption of calcium by the organs of the body such as kidneys and intestine. The thyroid gland is the largest endocrine gland that is situated prefrontal to the thyroid cartilage of the larynx in the neck. It regulates the calcium homeostasis and releases thyrocalcitonin hormone which is produced by the ‘C’ cells. The hormone is secreted when the calcium concentration in blood is high. They lower the calcium level by suppressing the release of calcium ions from the bones. Hence calcitonin has a contrary effect on calcium in comparison to the parathyroid hormone.
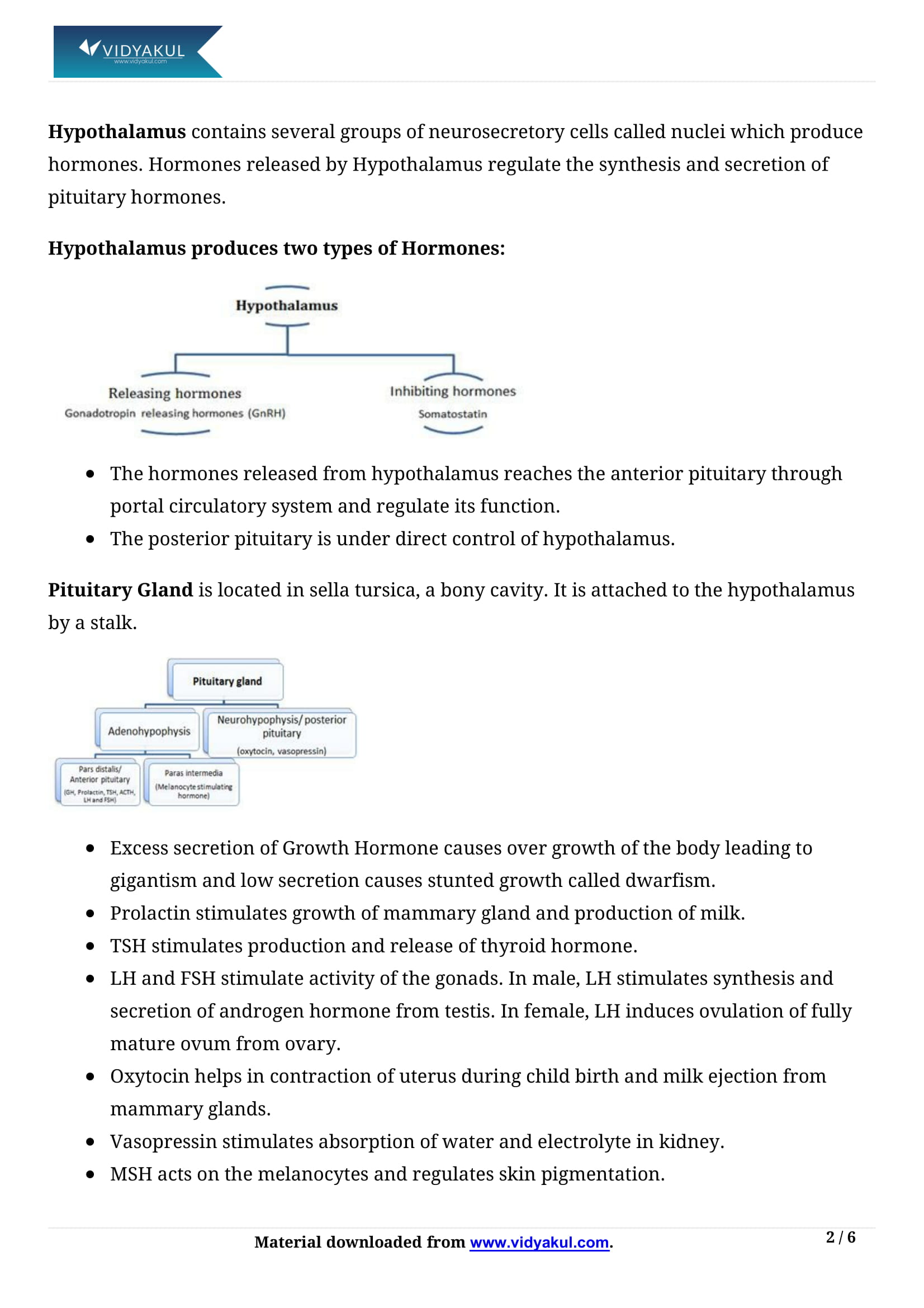
Explain why hypothalamus is a super master endocrine gland.
The hypothalamus controls an array of functions. It has many groups of neurosecretory cells known as nuclei that produce hormones. These hormones maintain the secretion and synthesis of pituitary hormones. The hormones produced by the hypothalamus are – the releasing hormones and the inhibiting hormones. The releasing hormones trigger the secretion of pituitary hormones and the inhibiting hormones hinder the secretions of the pituitary hormones. Through a portal circulatory system, the hormones arrive at the pituitary gland and check the functions of the anterior pituitary. Hypothalamus directly regulates the posterior pituitary. It also synthesizes two hormones – vasopressin and oxytocin which are further conveyed to the posterior pituitary.
What are the causes and symptoms of hormonal disorders?
Hormonal disorders or imbalance occurs when there is an under secretion or an oversecretion of respective hormones by the respective endocrine glands. There are several other environmental factors and medical conditions behind the cause of hormonal disorders in an individual and it varies with the age and sex. These factors include:
Obesity,
Cancers.
Allergies.
Poor diet.
Infections.
Benign tumours.
Intake of oral steroids.
Exposure to toxins, pollutants, and other chemicals.
The symptoms of a hormonal imbalance usually vary according to the type of hormones. The more common causes of hormonal imbalances are:
Fatigue.
Bloating.
Depression.
Headaches.
Puffy face.
Infertility.
Mood swings.
Blurred vision.
Sleep Disorders.
Increased thirst.
Reduced sex drive.
Excessive sweating.
Changes in appetite.
Tenderness of breast.
Brittle or weak bones.
Weight gain or weight loss.
Sensitivity to cold and heat.
Changes in the voice in females.
Dry skin, thinning and brittle hair.
Variations in blood pressure, blood sugar concentration and heartbeat.
Practice Questions
State the significance of luteinizing hormones in males and females.
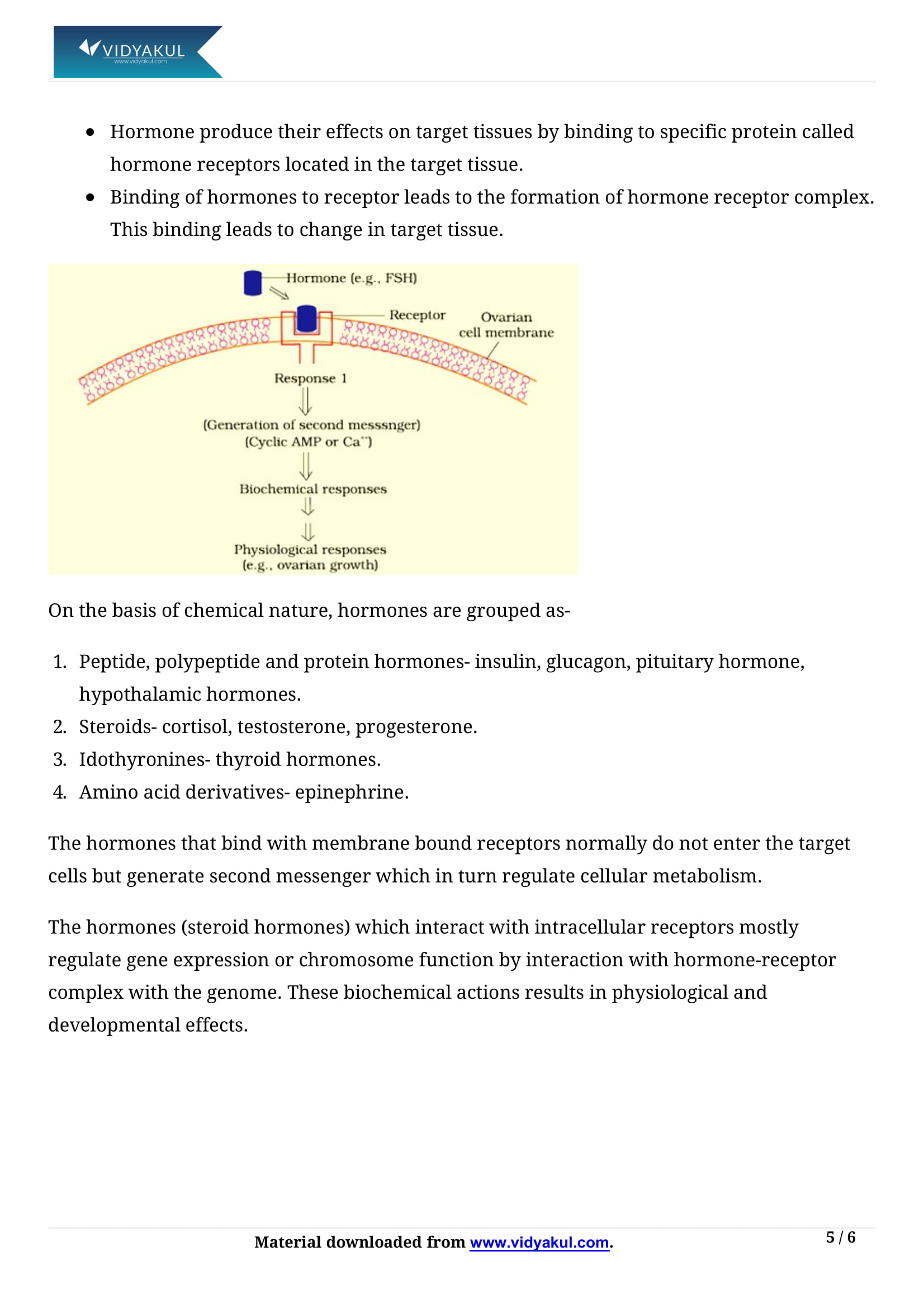
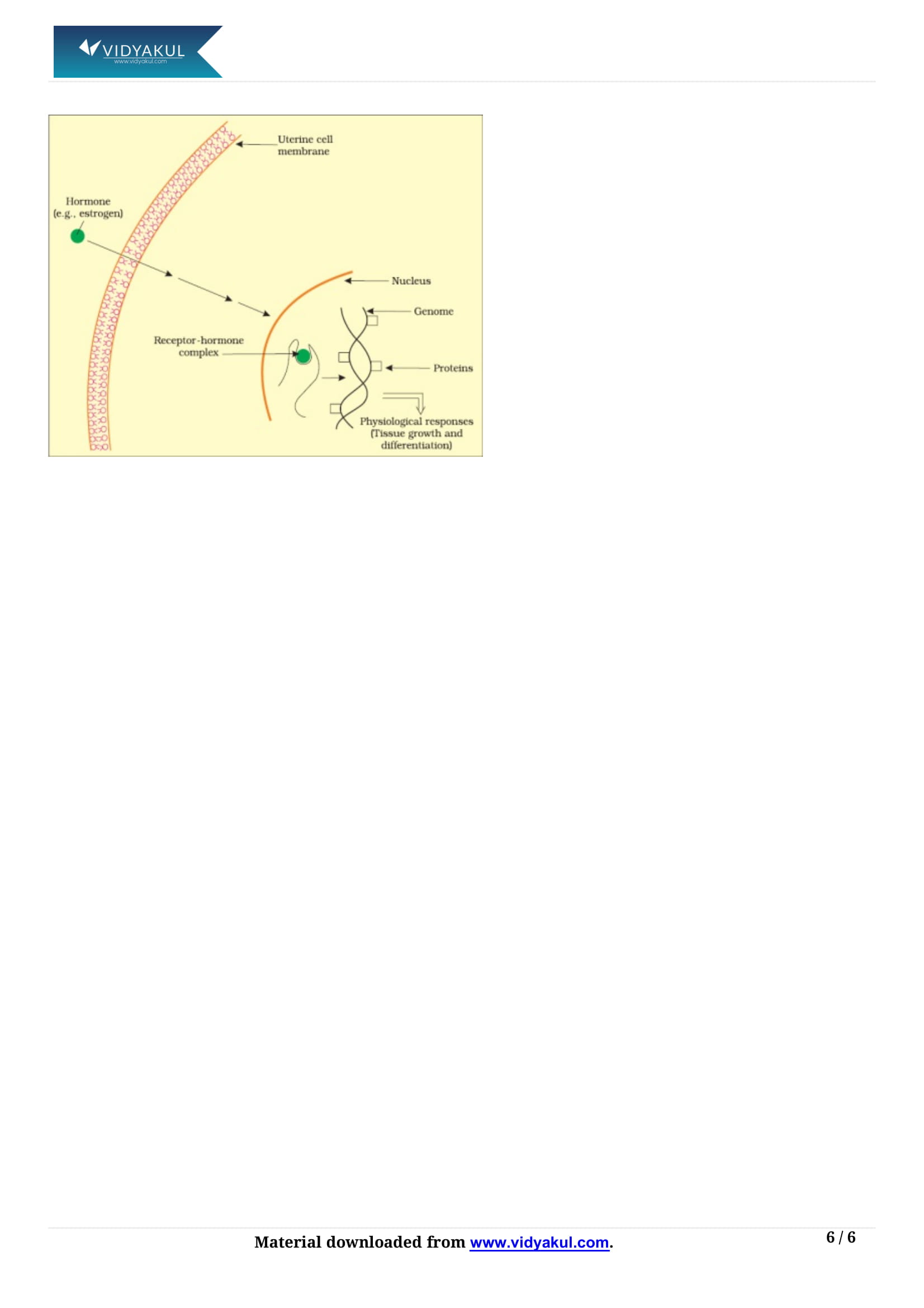
Write about the importance of the second messenger in hormone action.
Which is the steroid that controls inflammatory responses? Name its source and its other functions.
Why do old people have a weak immunity system?
How does hypothyroidism affect the maturation and development of a growing baby, generally seen during pregnancy?
Differentiate between hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism.
Endocrine Glands and Hormones: (i) There are two coordinating, integrating and interdependent systems in our body, namely the nervous system and endocrine system.
(ii) The endocrine system achieves coordination and integration by transmitting information through hormones also known as chemical messengers.
(iii) Endocrinology is the study of endocrine glands and hormones.
(iv) The term hormone was coined by Starling in 19051905. The endocrine system consists of hypothalamus, pituitary, pineal, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pancreas, thymus and gonads (testis and ovary).
(v) Some other organs, e.g., gastrointestinal tract, kidney, heart, etc., also produce hormones.
(vi) Prostaglandins are long chain unsaturated fatty acids which regulate vasoconstriction, vasodilation, contraction of uterine muscles, etc.
(vii) Pheromones are molecules used for chemical communication between individual animals.
Thyroid Gland: (i) The thyroid gland hormones play an important role in the regulation of the basal metabolic rate, development and maturation of the central neural system, erythropoiesis, metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and fats, menstrual cycle.
(ii) Another thyroid hormone, i.e., thyrocalcitonin secreted by C-cells regulates calcium levels in our blood by decreasing it.
A milkman’s cow refuses to give milk. On being fondled by the calf, the cow produced enough milk. Explain the significance of the endocrine gland and the pathway related to this response.
A urine sample contained increased content of glucose and ketone bodies. Answer the questions below basis this observation.
Describe the importance of hormones and endocrine glands responsible for regulating the Calcium Homeostasis.
Explain why hypothalamus is a super master endocrine gland.
What are the causes and symptoms of hormonal disorders?
Obesity,
Cancers.
Allergies.
Poor diet.
Infections.
Benign tumours.
Intake of oral steroids.
Exposure to toxins, pollutants, and other chemicals.
Fatigue.
Bloating.
Depression.
Headaches.
Puffy face.
Infertility.
Mood swings.
Blurred vision.
Sleep Disorders.
Increased thirst.
Reduced sex drive.
Excessive sweating.
Changes in appetite.
Tenderness of breast.
Brittle or weak bones.
Weight gain or weight loss.
Sensitivity to cold and heat.
Changes in the voice in females.
Dry skin, thinning and brittle hair.
Variations in blood pressure, blood sugar concentration and heartbeat.
State the significance of luteinizing hormones in males and females.
Write about the importance of the second messenger in hormone action.
Which is the steroid that controls inflammatory responses? Name its source and its other functions.
Why do old people have a weak immunity system?
How does hypothyroidism affect the maturation and development of a growing baby, generally seen during pregnancy?
Differentiate between hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism.
Learn more about it in Chemical Coordination and integration Class 11 Notes pdf.
Download this solution for FREE Download this PDF
Download Vidyakul App for more videos, PDF's and Free video lectures.