Solid State Class 12 Notes

Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solid State Notes – PDF Download
Chapter 1 The Solid State
It is an important chapter for CBSE 12th Board Students. Vidyakul's NCERT notes provide clear and precise answers to questions in the text, allowing students to understand the topic.
This chapter discusses the intermolecular forces between atoms and the characteristics of the solids around us and attempts to clarify the concepts of the general properties of solids and the difference between amorphous and crystalline solids and helps students understand the nature of solids. binding force in matter.
CBSE CLASS 12th CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 1 NOTES
Points to Remember
Below we have provided some of the important points from the NCERT notes for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1:
A solid is a type of matter but has a definite shape and volume.
Furthermore, any deviation from a perfectly ordered arrangement of constituent particles is referred to as a defect or imperfection.
When the ratio of cations to anions remains constant, stoichiometric flaws occur. The two types of defects are Schottky and Frenkel.
Non-stoichiometric defects happen when the cation-anion ratio shifts as a result of the defect. There are two types of this defect: metal excess and metal deficiency.
Doping is also the addition of impurities to crystalline solids in order to alter their properties.
Topics and Sub-Topics
The topics and sub-topics covered in Solid State Class 12 Notes are:
1.1 General Characteristics of Solid State
1.2 Amorphous and Crystalline Solids
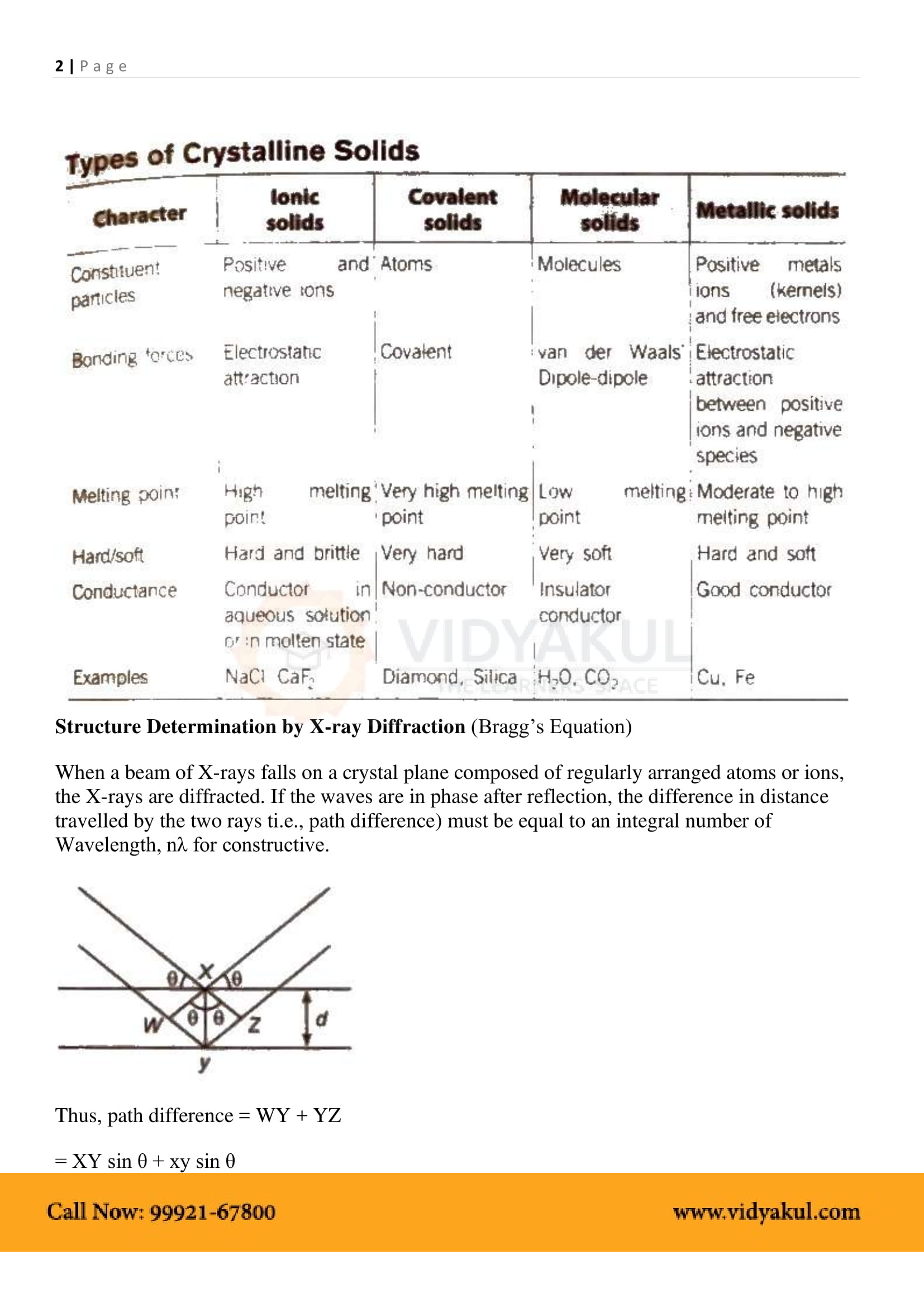
1.3 Classification of Crystalline Solids
1.3.1 Molecular Solids
1.3.2 Ionic Solids
1.3.3 Metallic Solids
1.3.4 Covalent or Network Solids
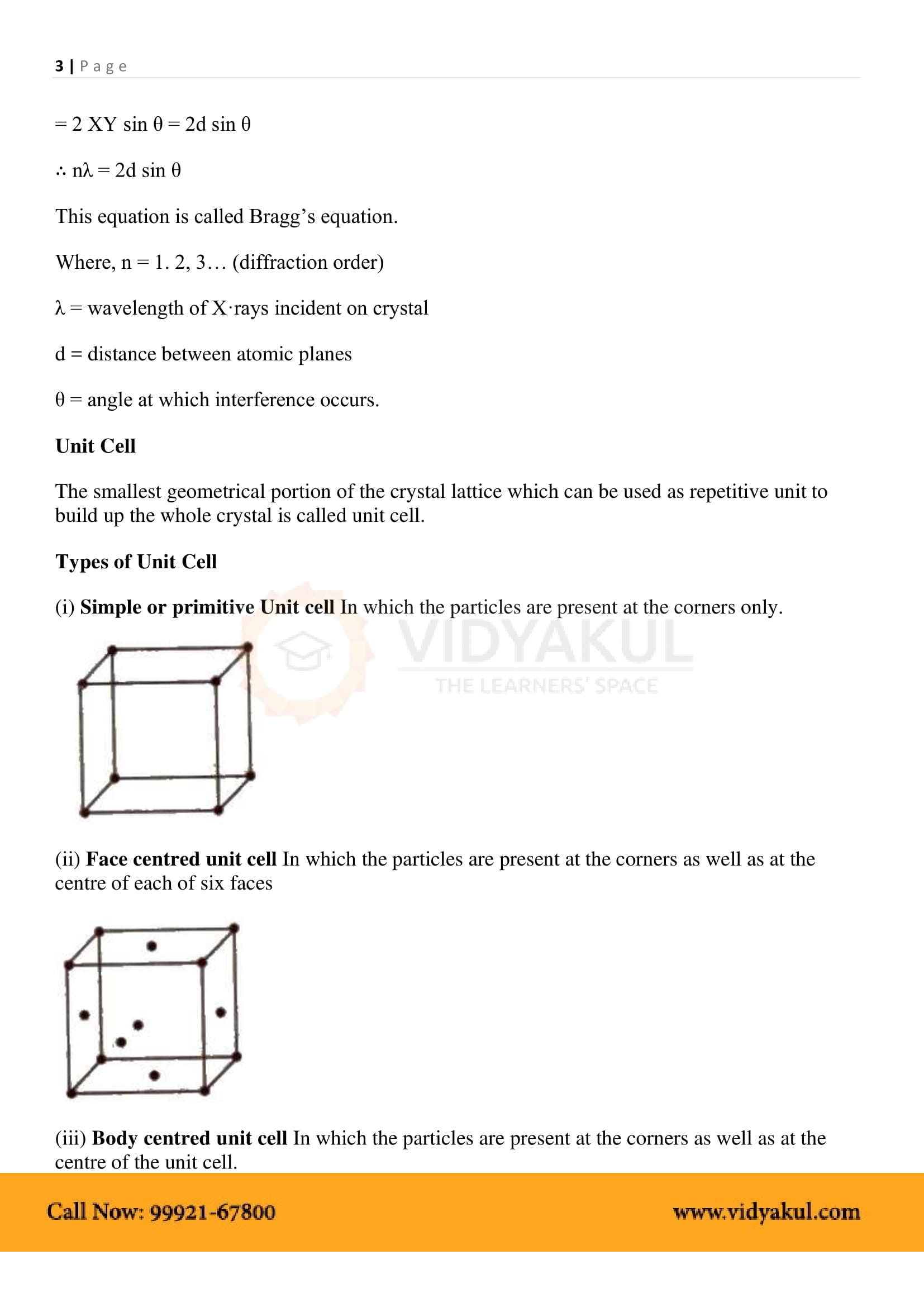
1.4 Crystal Lattices and Unit Cells
1.4.1 Primitive and Centred Unit Cells
1.5 Number of Atoms in a Unit Cell
1.5.1 Primitive Cubic Unit Cell
1.5.2 Body-Centred Cubic Unit Cell
1.5.3 Face-Centred Cubic Unit Cell
1.6
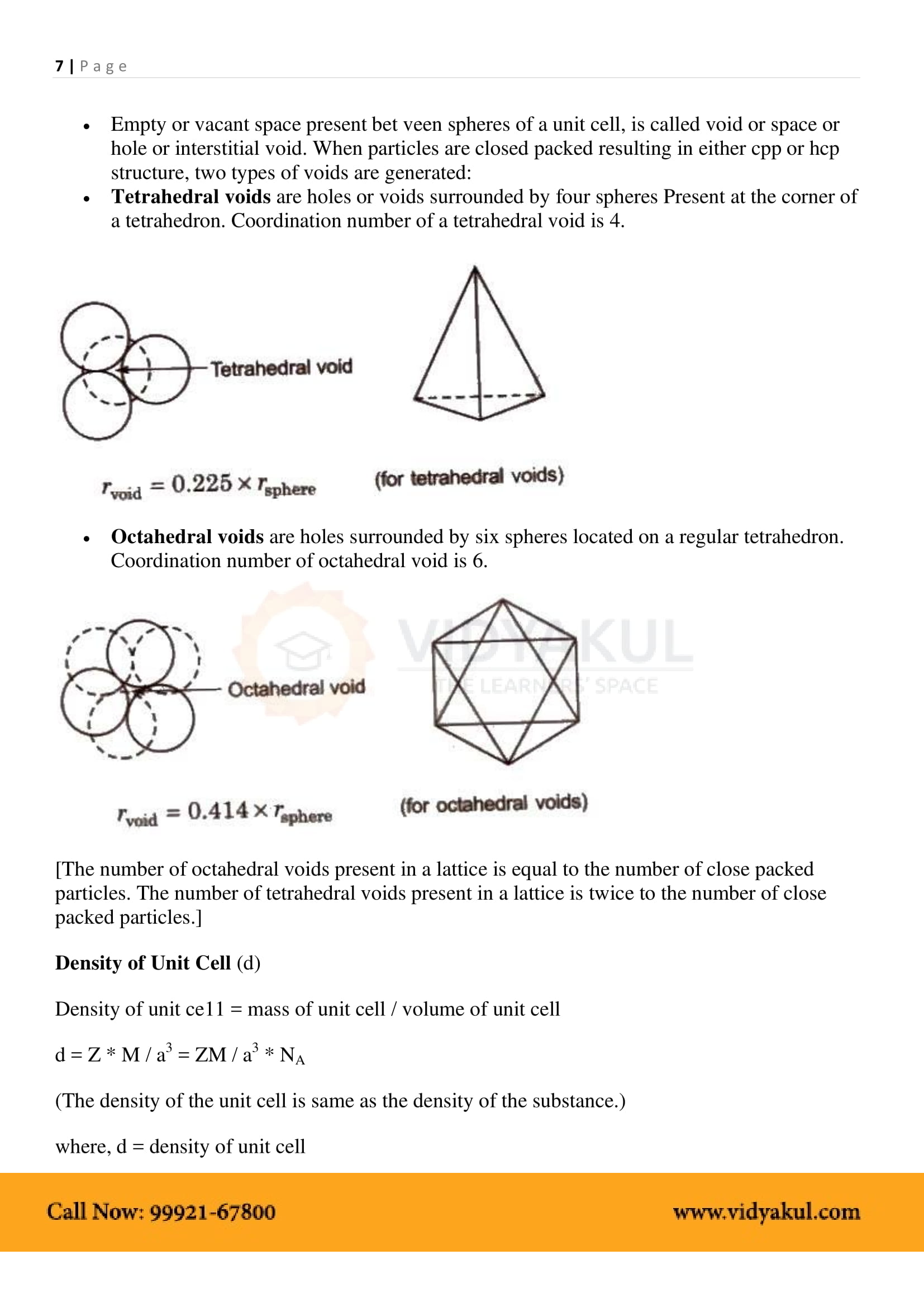
1.6.1 Formula of a Compound and Number of Voids Filled
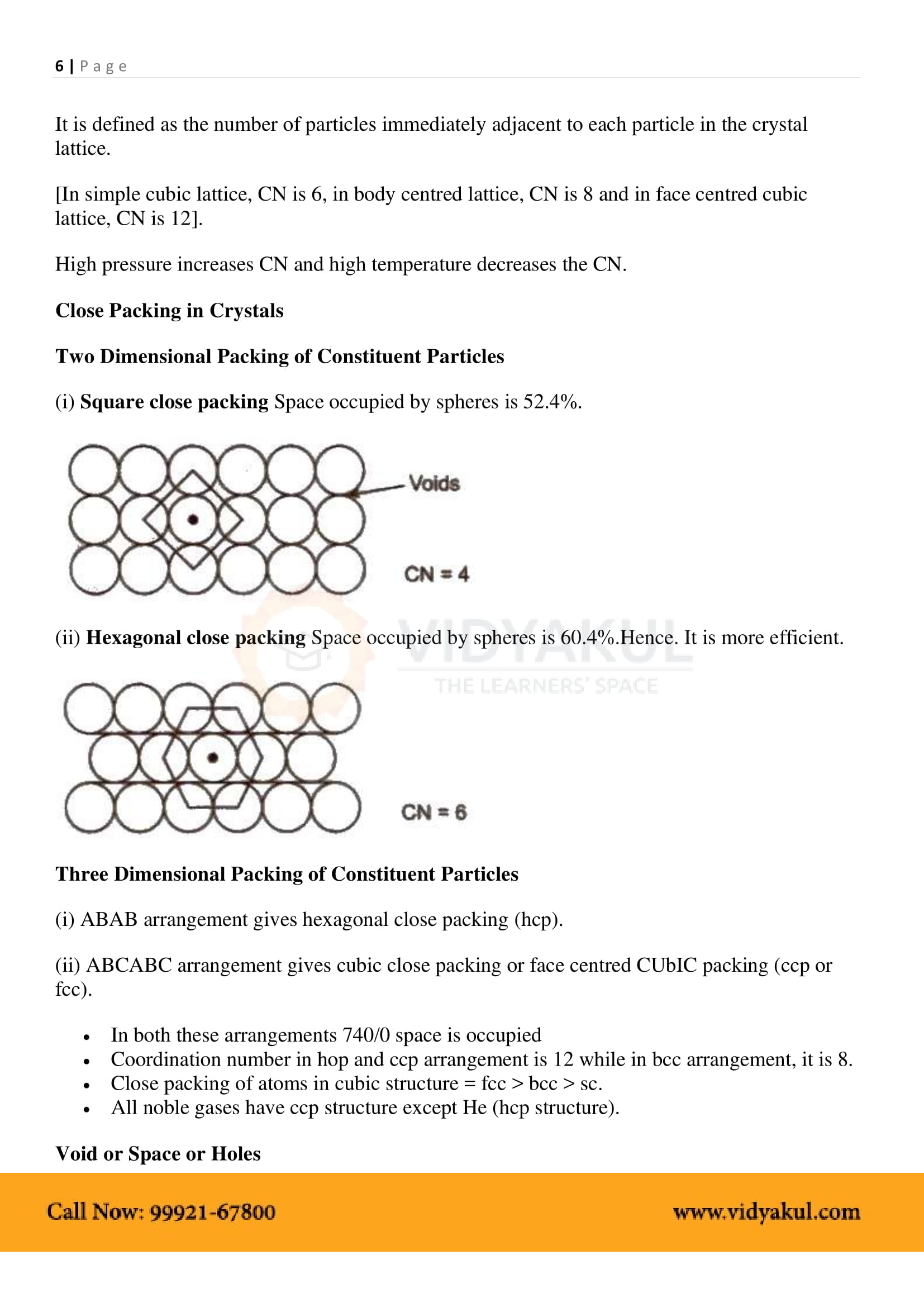
1.7 Packing Efficiency
1.7.1 Packing Efficiency in hcp and
1.7.2 Efficiency of Packing in Body-Centred Cubic Structures
1.7.3 Packing Efficiency in Simple Cubic Lattice
1.8 Calculations Involving Unit Cell Dimensions
1.9 Imperfections in Solids
1.9.1 Types of Point Defects
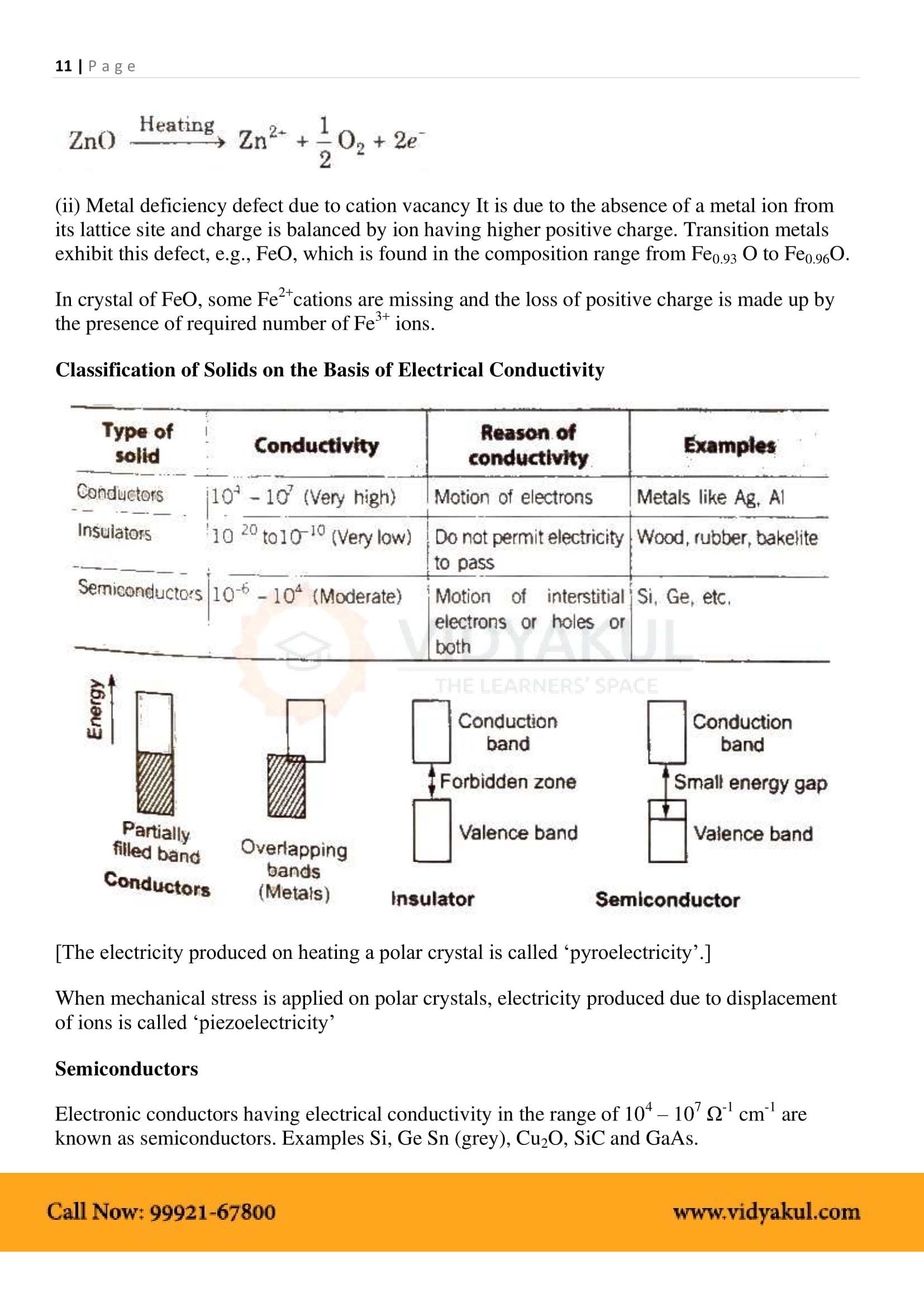
1.10 Electrical Properties
1.10.1 Conduction of Electricity in Metals
1.10.2 Conduction of Electricity in Semiconductors
1.11 Magnetic Properties.
Download this solution for FREE Download This PDF
Download Vidyakul App for more Important notes, PDF's and Free video lectures.






Few Important Questions
What are ‘Crystalline solids’?
Crystalline solids are solids whose constituents are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure forming a crystal lattice.
What is a ‘Unit cell’?
A unit cell is the smallest portion of a crystal lattice that shows the three-dimensional pattern of the entire crystal.
What is ‘Packing Efficiency’?
The packing efficiency is the fraction of the crystal/unit cell actually occupied by the atoms.
Practice Questions
Explain the term coordination number.
Distinguish between Cubic close-packing and Hexagonal close-packing.
Explain why Ionic solids are brittle and hard.
Distinguish between a semiconductor and a conductor.
Explain Paramagnetism with a suitable example.
What are ‘Crystalline solids’?
What is a ‘Unit cell’?
What is ‘Packing Efficiency’?
Explain the term coordination number.
Distinguish between Cubic close-packing and Hexagonal close-packing.
Explain why Ionic solids are brittle and hard.
Distinguish between a semiconductor and a conductor.
Explain Paramagnetism with a suitable example.



