Solutions Class 12 Notes

Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Solutions Notes – PDF Download
Chapter 2 Solution Notes
The NCERT notes for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 is solution-based. They are designed by experts according to the latest CBSE program to help students. Various important concepts are covered, such as solution types, solubility, binding properties, Raoult's law, and more. Vidyakul offers more than practice questions per sub-topic to help students prepare for the exam. Students coming to the exam must answer all these practical questions. Scroll down for more details. These NCERT notes will help students gain a competitive edge.
CBSE CLASS 12th CHEMISTRY 2 NOTES
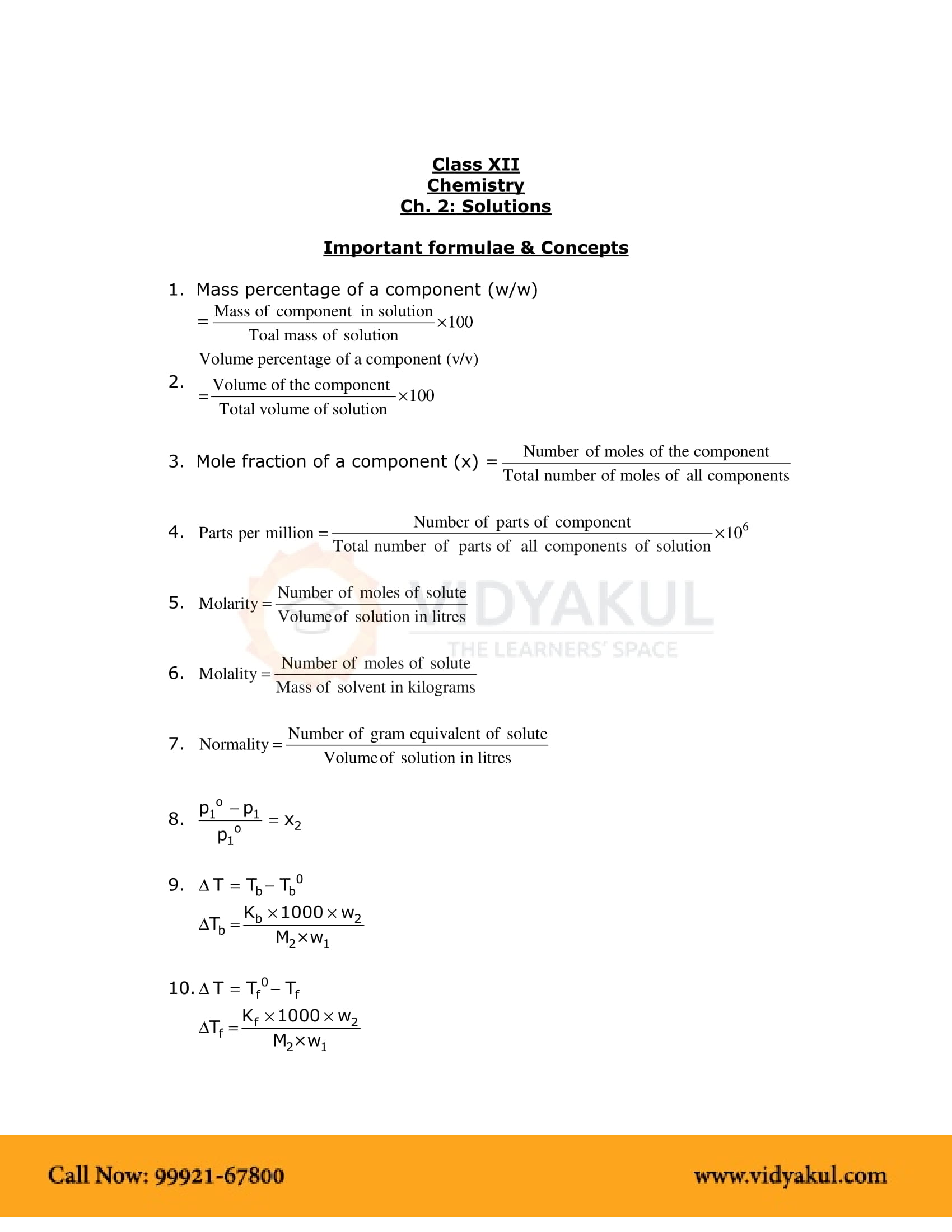
Points to Remember
NCERT Notes for Grade 12 Chemistry Chapter 2: Important Points:-
A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more non-chemically reactive substances whose composition can vary within certain limits.
Henry's Law: The mass of a gas dissolved in a given volume of liquid at constant temperature is directly proportional to the pressure of the gas at equilibrium with the liquid or to a mixture of gases at In equilibrium with a liquid, the partial pressure of a Gas is proportional to the mole fraction of a gas in a solution.
Raoult's law in its general form can be stated as, for any solution, the partial vapor pressure of each volatile component in the solution is proportional to its molar fraction.
Solvents and solutes. In a binary solution, the component in smaller amounts is known as the Soluble, while the component in larger quantities is known as the Solvent. If water is the solvent, the solution is called an aqueous solution.
Topics and Sub-Topics
Click on the topic-wise links provided in the table below to get access to the NCERT Chemistry Chapter 2 chapter-wise important questions:
Download Vidyakul App for more Important videos, PDF's and Free video lectures.

Few Important Questions
What are the different types of solutions?
The 3 main types of solutions are: 1. Solid 2. Liquid 3. Gas
What are ‘Ideal solutions’?
When a solution obeys Raoult’s law over the entire range of concentrations it is called an ideal solution.
What is ‘Molarity’?
Molarity or molar concentration, is the concentration of a solution measured as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution.
Practice Questions
What is mole fraction?
Explain the role of molecular interaction in a solution of water and alcohol?
Give the statement of Henry’s law. List some applications.
What is a solution? Explain the different types of solutions.
What is molarity?



