Electrochemistry Class 12 Notes

Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3 Electrochemistry Notes – PDF Download
Chapter 3 Electrochemistry Notes
NCERT notes provide step-by-step explanations for all questions and solving them will help maximize student scores. After practicing the questions of electrochemistry, students will become proficient in areas such as electrochemical cells, galvanic cells, and electrolytic cells. Practicing electrochemistry-related questions will help students score well in CBSE Grade 12 Chemistry exams and also help them pass competitive exams like JEE, NEET, etc. Measure electrode potential, Nernst equation, primary and secondary batteries, and more. Vidyakul offers a set of over 400 practice questions for all the sub topics covered in Chapter 3. All questions in the text must be practiced without a high score. Scroll down to see NCERT notes for Grade 12 Chemistry Chapter 3.
CBSE CLASS 12th CHEMISTRY 3 NOTES
Points to Remember
Below is the list of important topics included in Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3 Electrochemistry.
Points to Remember
Students can find the important points to remember from NCERT Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3, as mentioned below. Going through the points before final exams helps students to have a quick revision of Chapter 3 Chemistry.
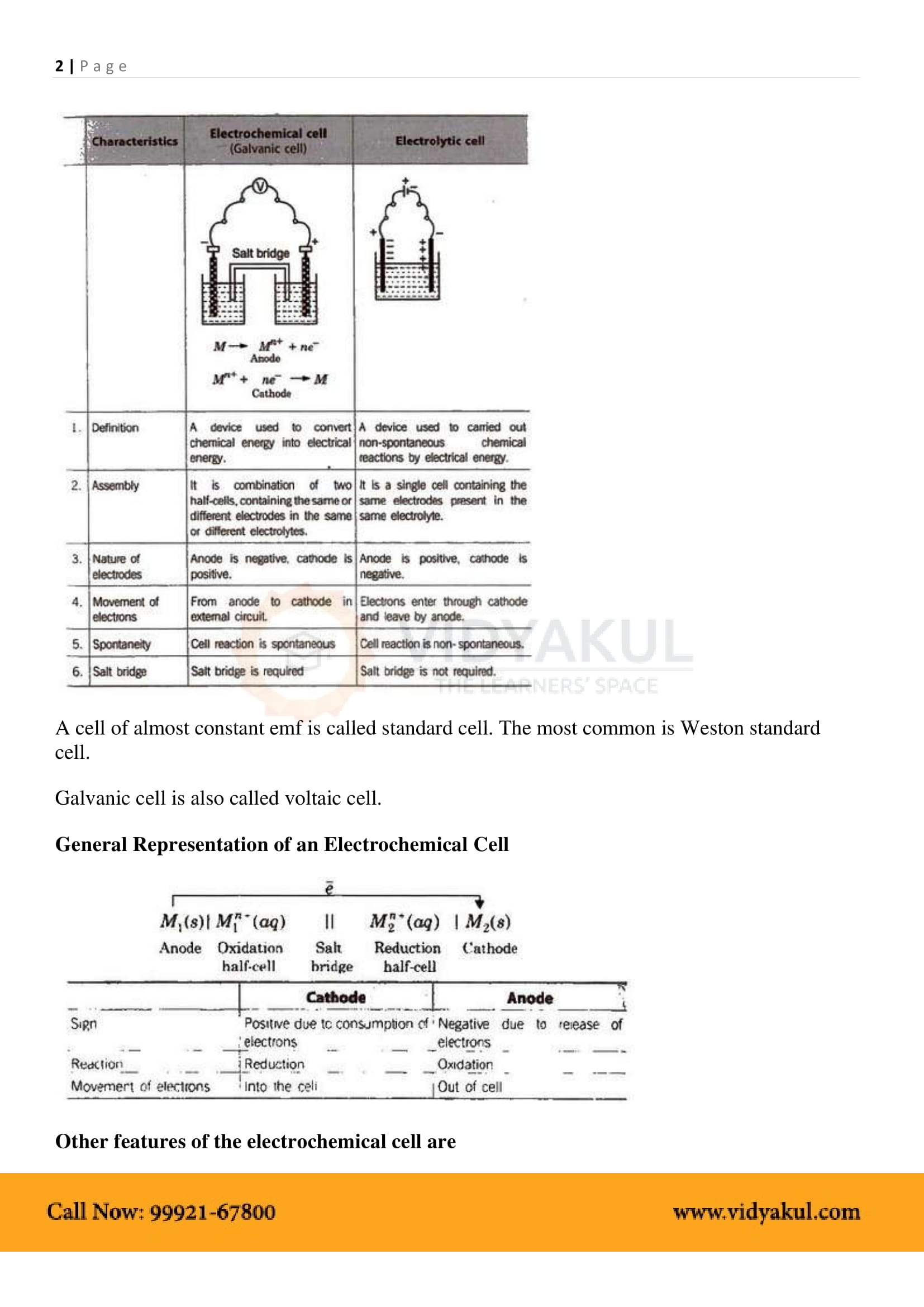
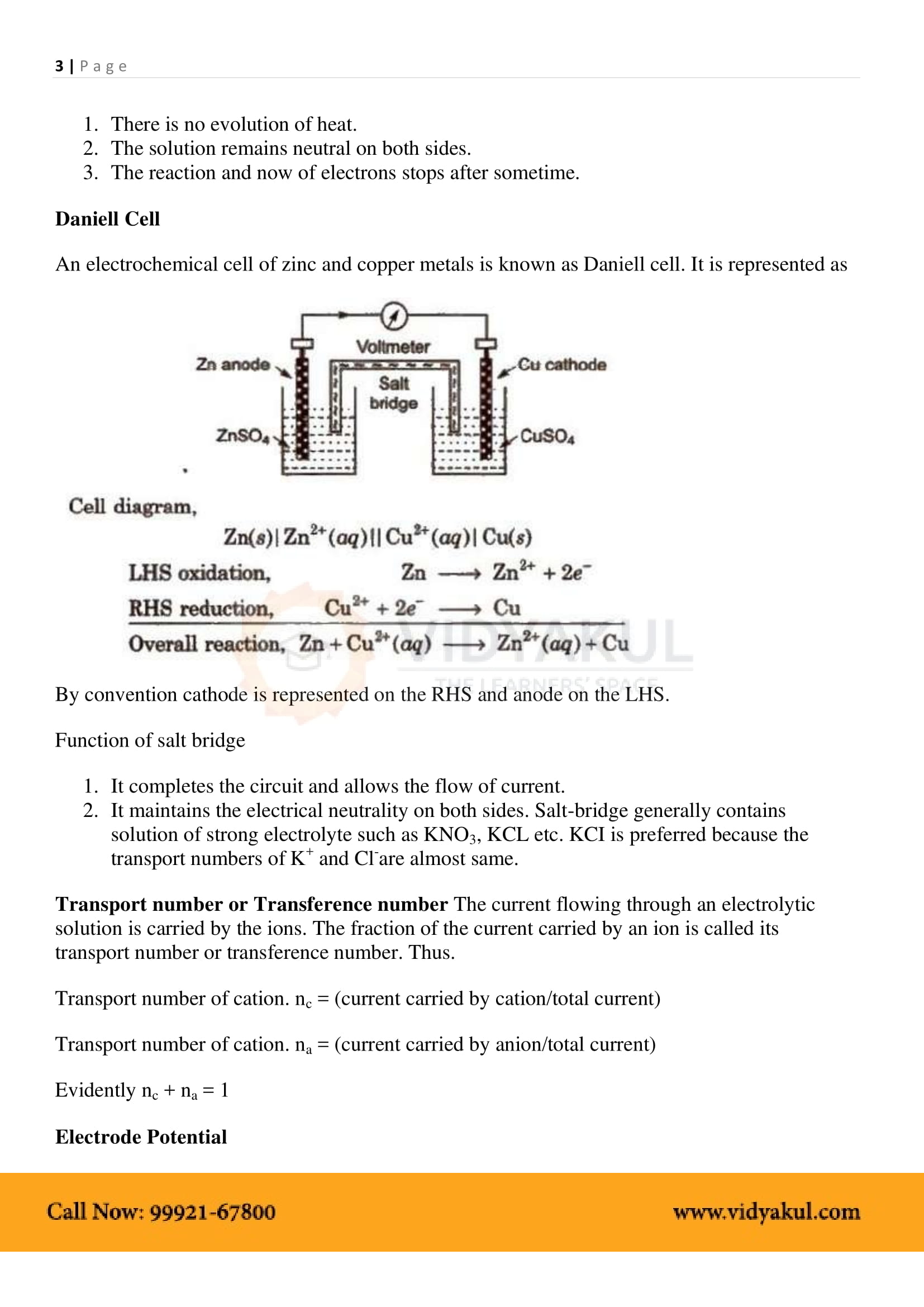
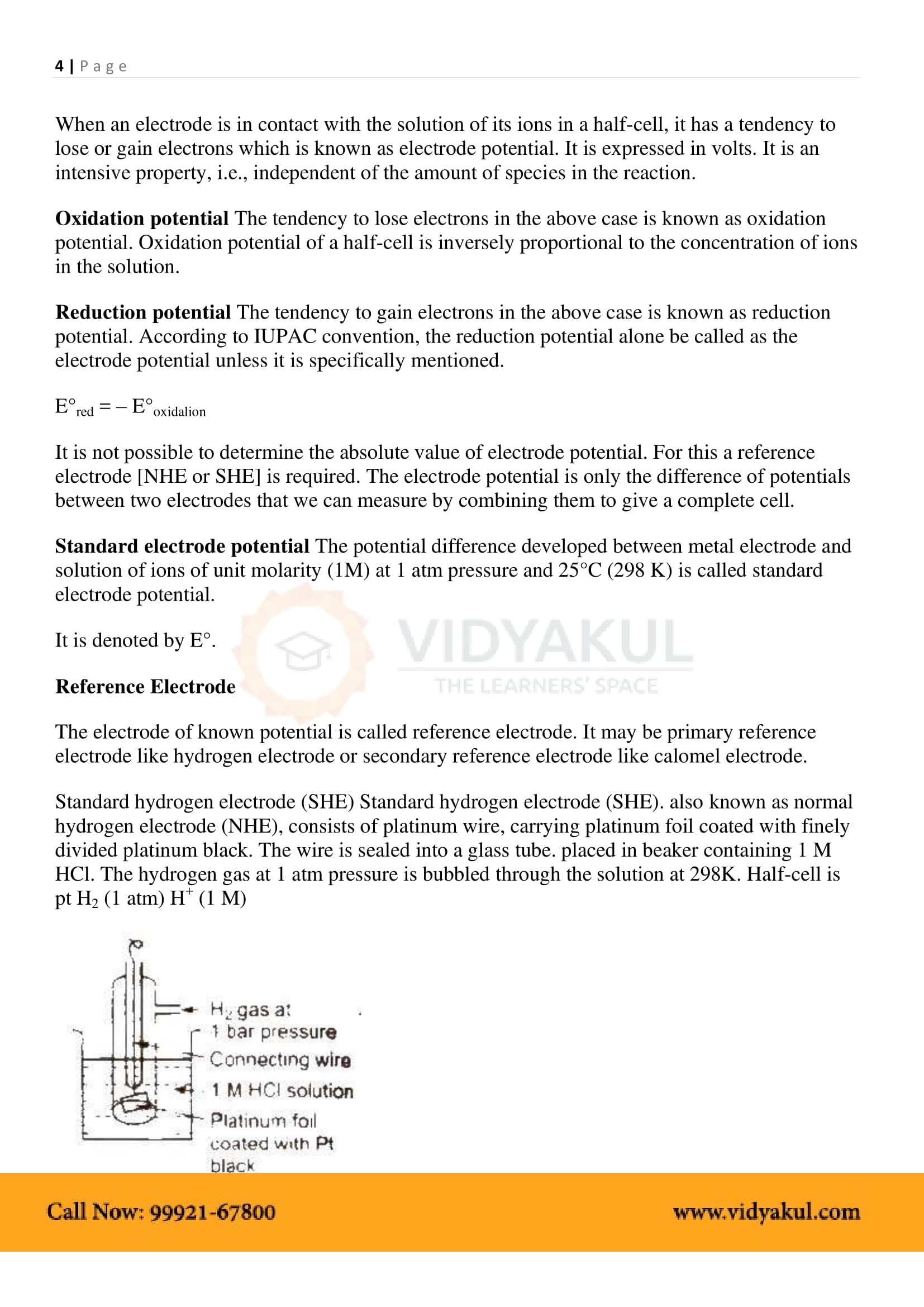
Electrochemical Cell: A device that converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
Anode: In electrochemical cells, the anode is the electrode at which oxidation takes place. It is the negative terminal.
Cathode: In electrochemical cells, the cathode is the electrode at which reduction takes place. It is the positive terminal.
EMF of the cell or Ecell = Ecathode −Eanode .
Thermodynamic Efficiency of Cell: It is the ratio of Gibb’s energy change to the enthalpy change of the cell reaction η = ΔG/ΔH.
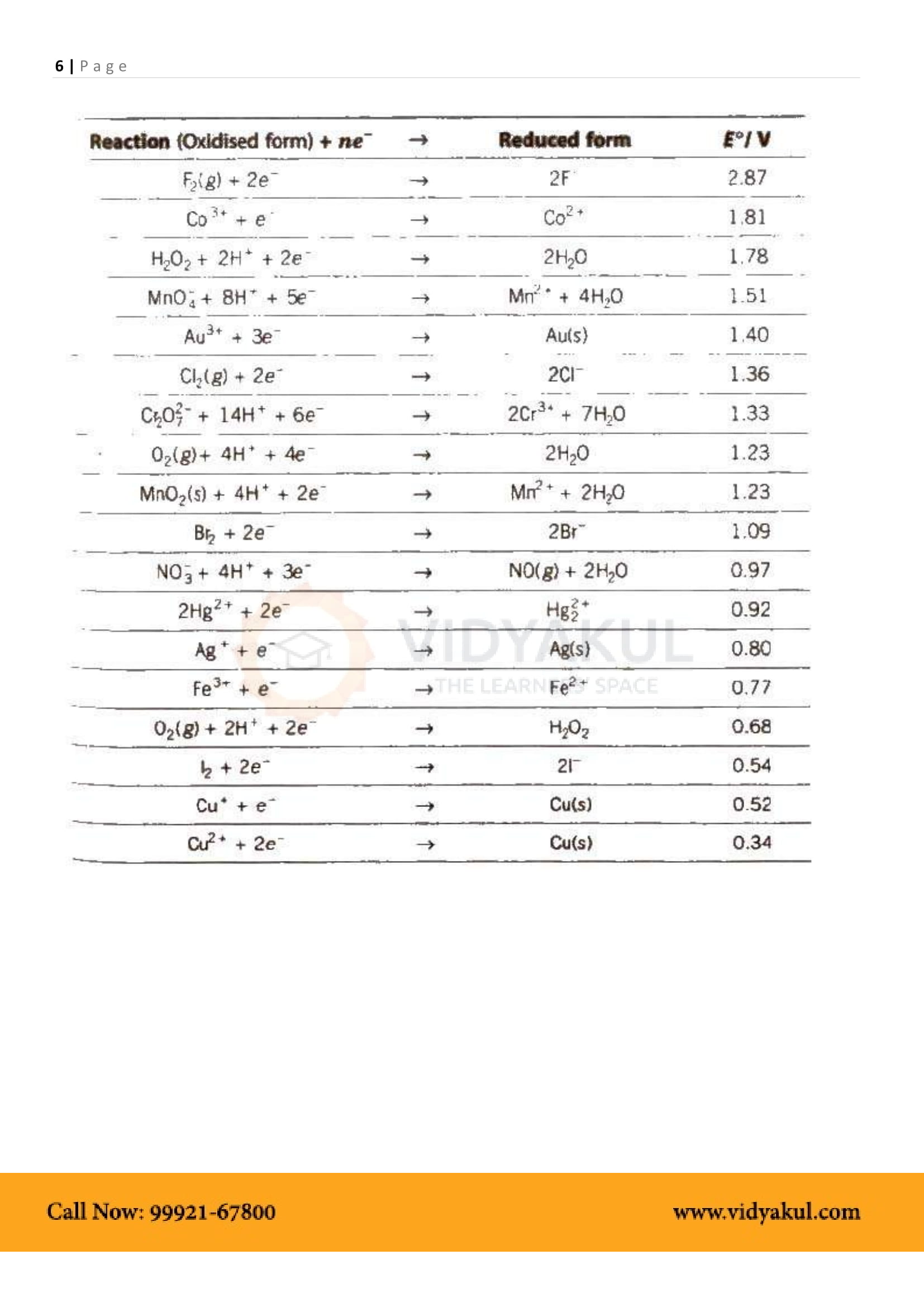
Electrochemical Series: Arrangement of various elements and electrode reactions in the increasing order of their reduction potentials.
Electrolyte: A substance that dissociates in solution to produce ions and hence conducts electricity in a dissolved state or molten state.
Molar Conductivity: Conductance of a solution containing one mole of the electrolyte, placed between two parallel electrodes one cm apart.
Topics and Sub-Topics
Below is the list of important topics included in Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3 Electrochemistry.
Download this solution for FREE Download This PDF
Download Vidyakul App for more notes, PDFs and Free video lectures.












Few Important Questions
What is a ‘Galvanic cell’?
Galvanic cell is an electrochemical cell in which an electric current is generated from spontaneous oxidation-reduction reactions.
What is ‘EMF’?
Electromotive force is equal to the terminal potential difference when no current flows.
What is ‘Reduction potential’?
Reduction potential is the a tendency of a chemical species to be reduced by gaining an electron.
Practice Questions
Define and distinguish between molar conductivity and conductivity.
How much charge is required to reduce 1 mol of Al3+ to Al?
How much electricity is necessary for the oxidation of 1 mol of H2O to O2 in a coulomb?
Find the cell constant of 0.001M KCl solution with the following details:
T = 208 K, conductivity = 0.146 × 10–3 S cm–1, R = 1500 Ω
Calculate the molar conductivity for the following:
Conductivity = 0.0248 S cm–1, 0.20 M solution of KCl solution, Temperature = 298 K
What is a ‘Galvanic cell’?
What is ‘EMF’?
What is ‘Reduction potential’?
Define and distinguish between molar conductivity and conductivity.
How much charge is required to reduce 1 mol of Al3+ to Al?
How much electricity is necessary for the oxidation of 1 mol of H2O to O2 in a coulomb?
Find the cell constant of 0.001M KCl solution with the following details:
Calculate the molar conductivity for the following:




