Chemical Kinetics Class 12 Notes

Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Kinetics Notes – PDF Download
Chapter 4 Chemical Kinetics Notes
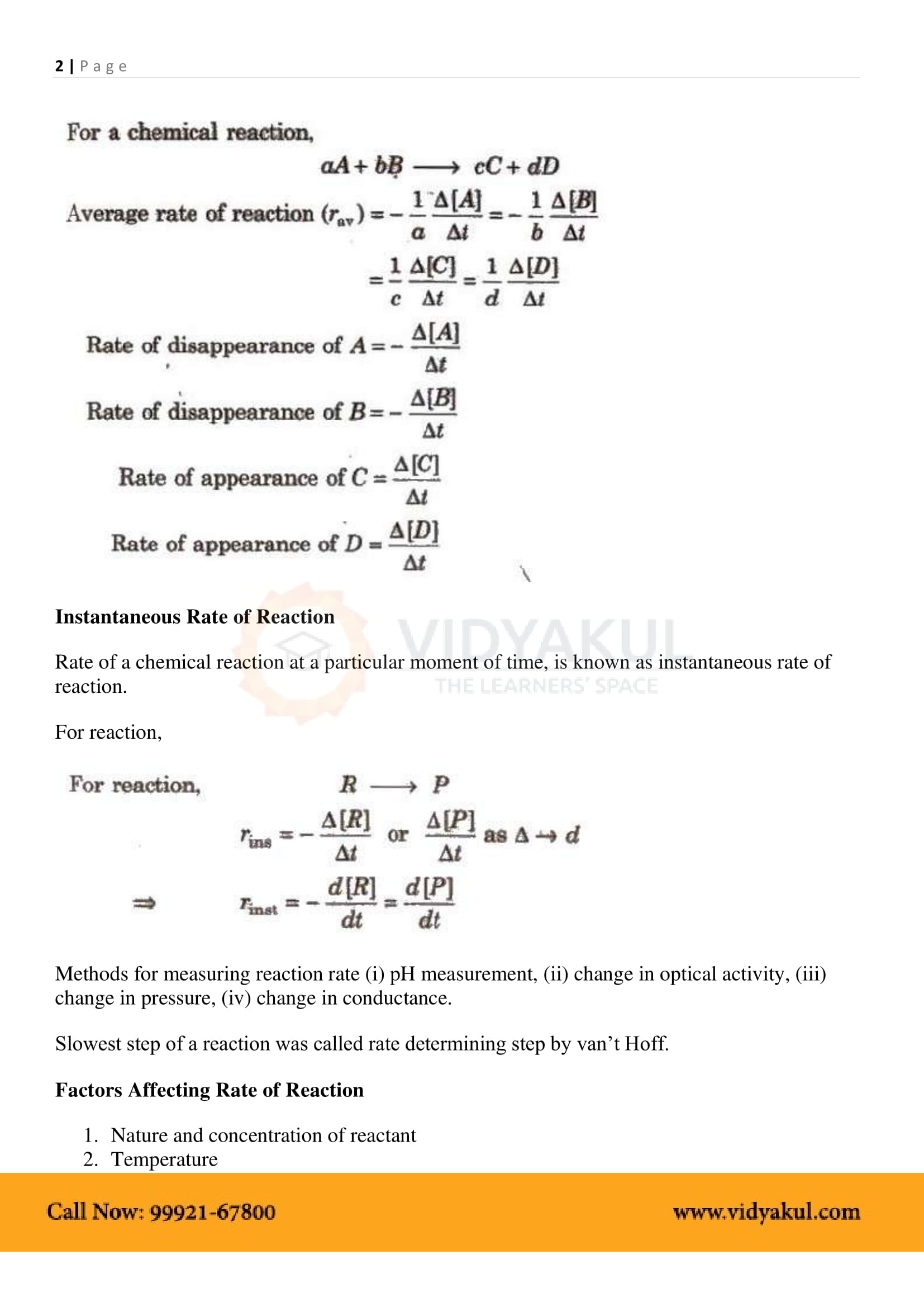
The study of chemical reactions involving reaction rates, formation of intermediates, rearrangements of atoms, and the influence of various variables is called chemical kinetics. The factors that affect the reaction rate are the catalyst concentration of the reactants and the temperature. The reaction rate cannot be predicted but must be determined experimentally. The rate law gives a mathematical representation of the reaction rate.
CBSE CLASS 12th CHEMISTRY 4 NOTES
Points to Remember
NCERT notes for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4: Important Points to Remember:-
Chemical kinetics is a branch of chemistry concerned with the study of reaction rates and their mechanisms.
A molecule refers to the number of reactive species that collide simultaneously to cause a chemical change.
A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself undergoing any chemical change.
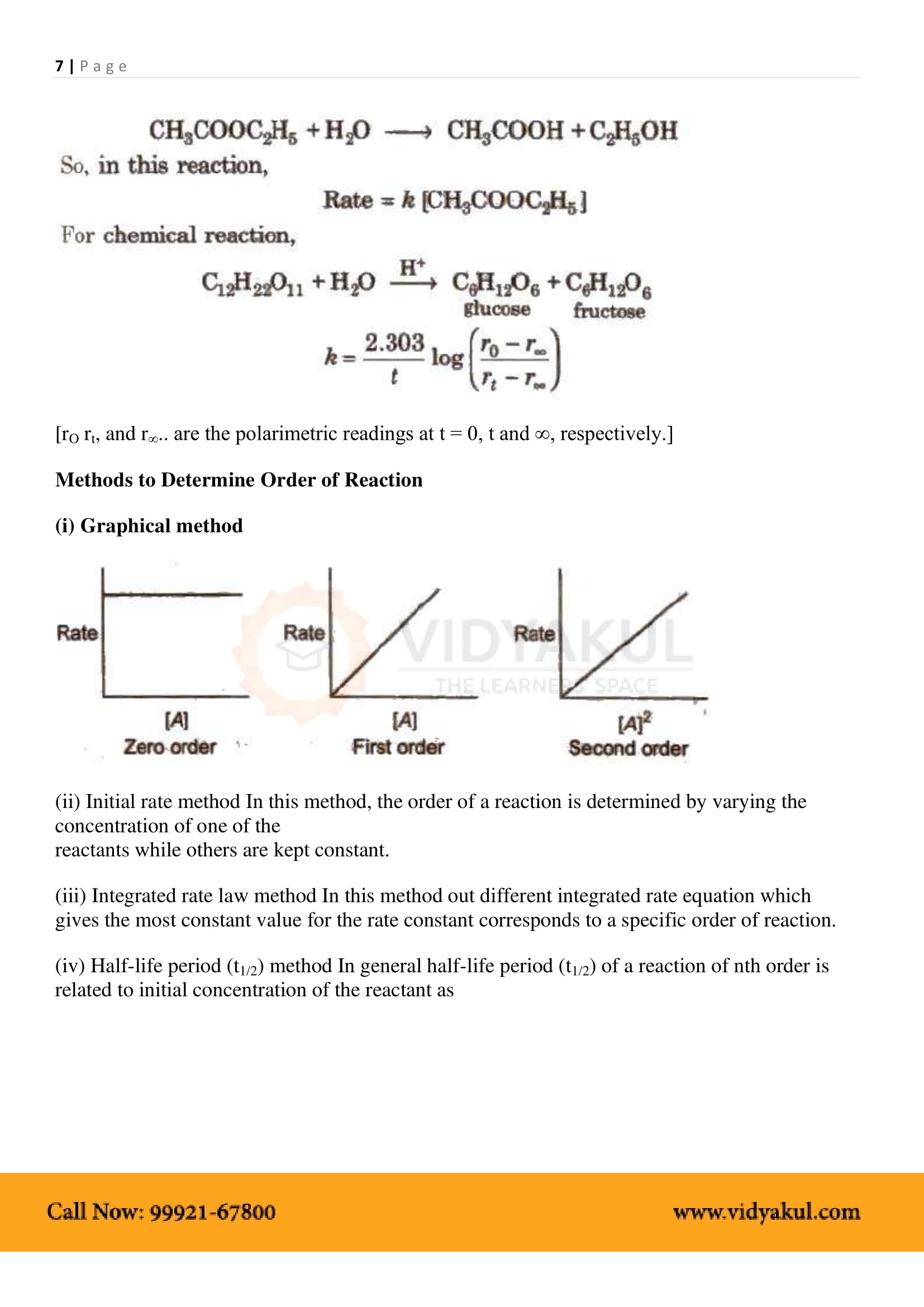
Integrated rate equations refer to built-in differential rate equations that give the relationship between the rate constant and the concentration at different times.
The reaction rate is the rate of change in the attention of one of the reactants or products over time at a given time.
Topics and Sub-Topics
The fourth chapter of Chemistry deals with Chemical Kinetics. Designed as per the latest syllabus, the NCERT notes for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 will make it easier for the students to prepare for the examinations. It will allow the students to easily revise the entire chapter.
Click on the topic-wise links provided in the table below to get access to the CBSE Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Kinetics chapter-wise important questions:
Few Important Questions
What the main functions of ‘Surface Chemistry’?
Enzymatic reactions at the biological interfaces found in the cell walls and membranes. In the electronics industry, they are used in the surface and interface of microchips found in computers.
What is ‘Arrhenius equation’?
The Arrhenius equation describes the relation between the rate of reaction and temperature for many physical and chemical reactions.
What is the ‘Rate of a reaction’?
Rate of a reaction is the speed at which a chemical reaction proceeds.
Practice Questions
Calculate the rates of production of H2 and N2 if the decomposition of NH3 on a platinum surface is a zero-order reaction. k = 2.5 × 10–4 mol–1 L s–1
The given equation log k = 14.34 – 1.25 × 104K/T is the rate constant for the first-order decomposition of H2O2. Find Ea and temp at which its half period will be equal to 256 minutes.
Show that, for a first-order reaction, the time needed to complete 99 percent is double the time needed to complete a 90 percent reaction.
Calculate the half-life of a first-order reaction for the rate constant 200 s–1.
What the main functions of ‘Surface Chemistry’?
What is ‘Arrhenius equation’?
What is the ‘Rate of a reaction’?
Calculate the rates of production of H2 and N2 if the decomposition of NH3 on a platinum surface is a zero-order reaction. k = 2.5 × 10–4 mol–1 L s–1
The given equation log k = 14.34 – 1.25 × 104K/T is the rate constant for the first-order decomposition of H2O2. Find Ea and temp at which its half period will be equal to 256 minutes.
Show that, for a first-order reaction, the time needed to complete 99 percent is double the time needed to complete a 90 percent reaction.
Calculate the half-life of a first-order reaction for the rate constant 200 s–1.
Download this solution for FREE Download This PDF